Using defocus-induced circle of confusion features for dust particle size measurement on mirrors
-
摘要:
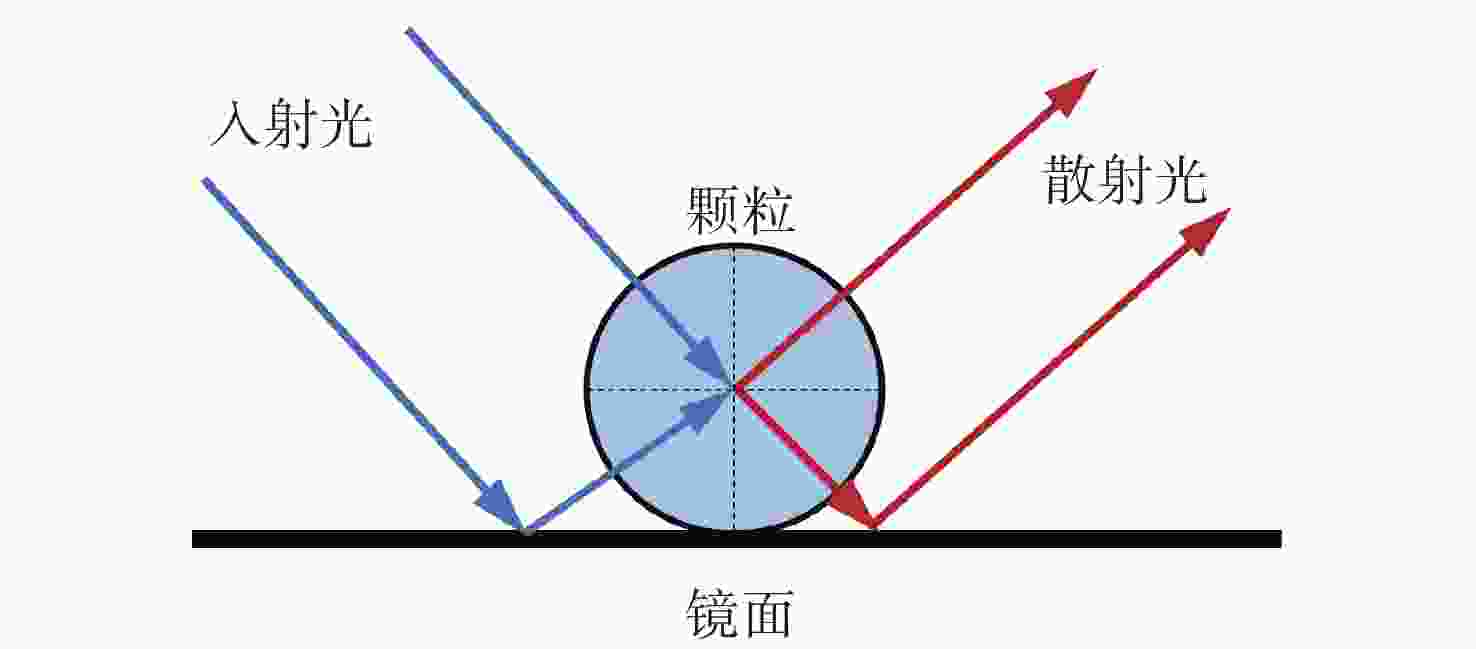
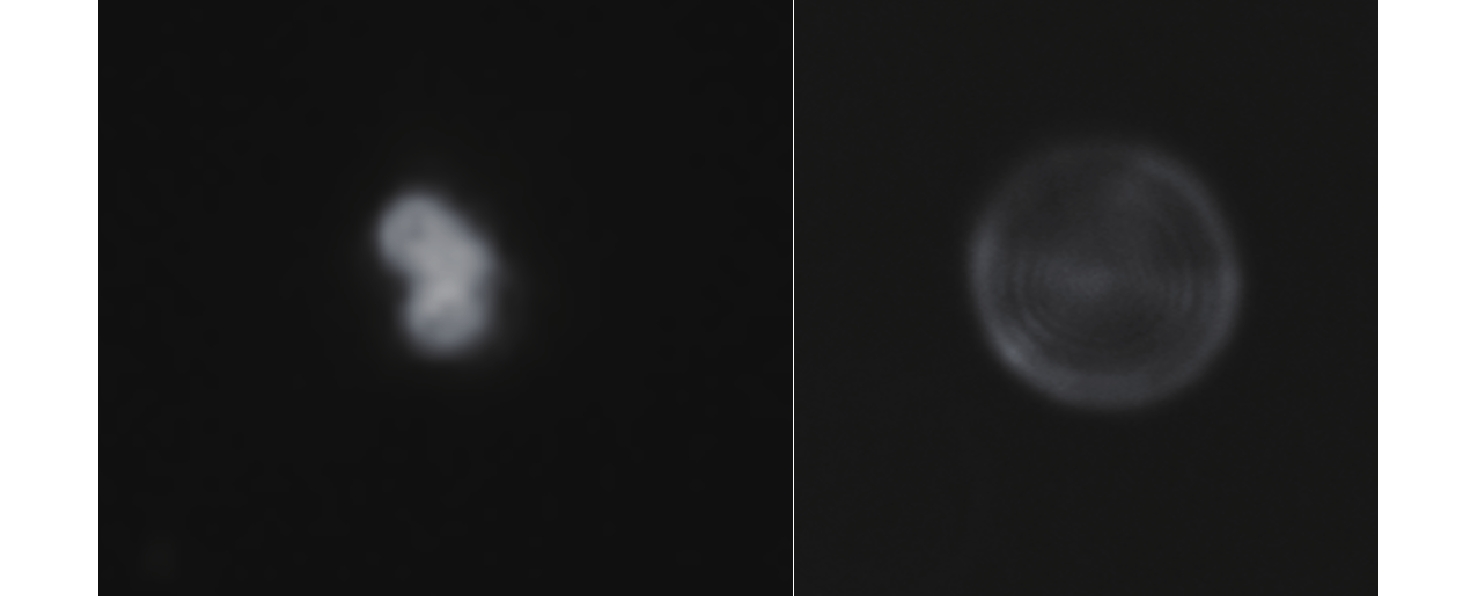
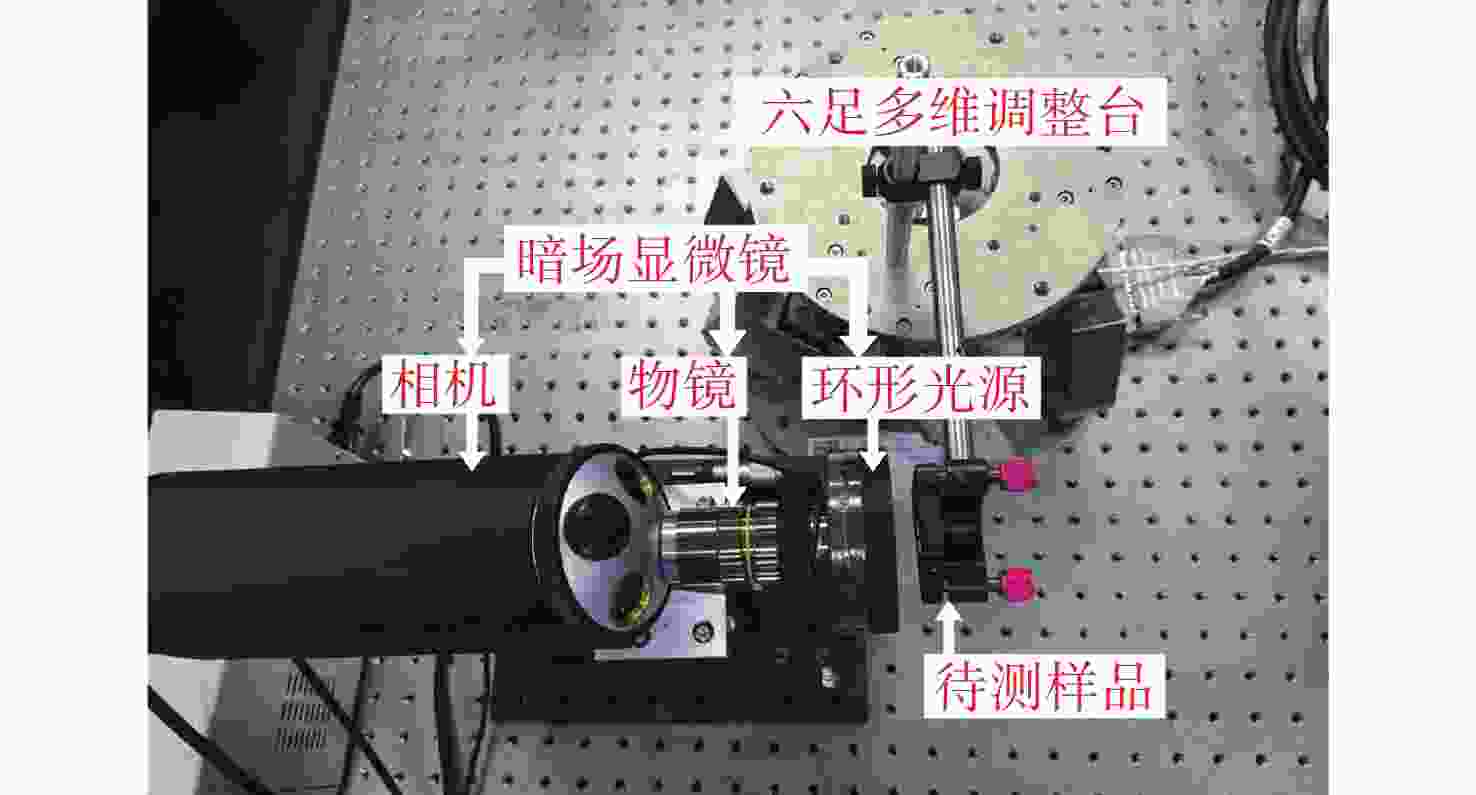
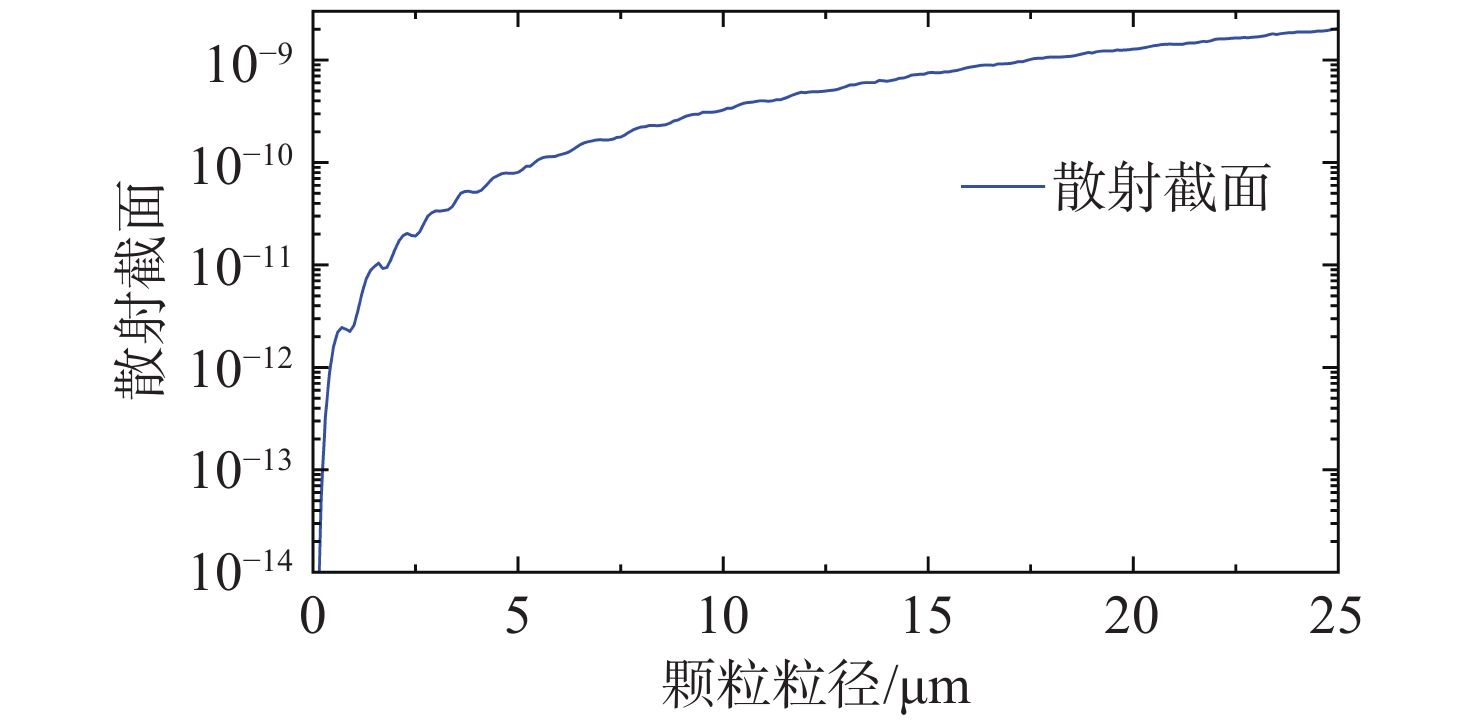
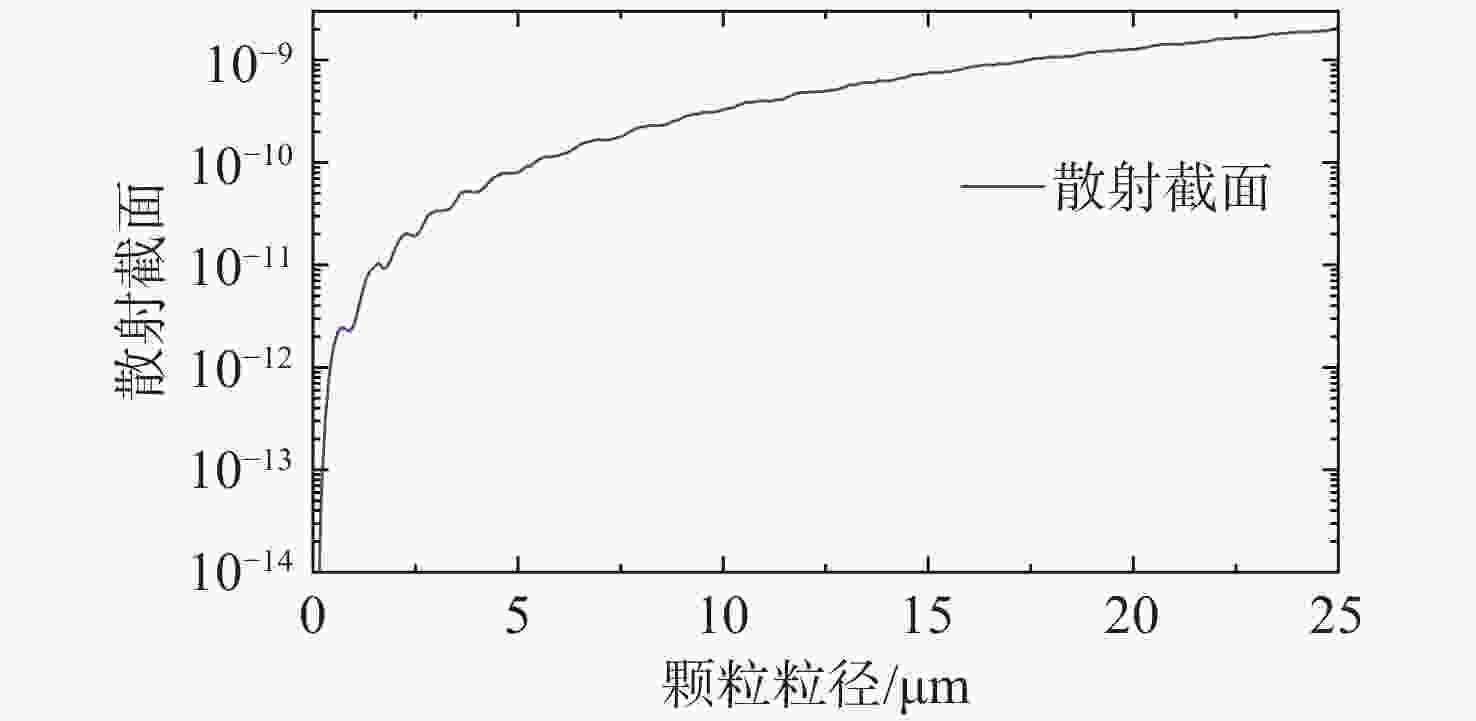
光学表面颗粒污染检测是保障空间望远镜成像性能的重要措施。传统颗粒污染检测常使用暗场散射显微镜拍摄颗粒图像,再对图像中颗粒外轮廓作外接圆计算颗粒尺寸。该方法要求拍摄过程严格对焦,对不规则形状的颗粒尺寸检测结果误差较大。为了提高检测镜面上微小颗粒尺寸的精度,消除对焦不准和颗粒形状差异带来的误差。本文提出利用离焦诱导的弥散圆检测颗粒尺寸的方法。利用颗粒尺寸与颗粒散射能量的对应关系,通过离焦将颗粒的暗场散射图像变成弥散圆。最后分析颗粒离焦弥散圆特征来测量颗粒的真实尺寸。该方法可以规避颗粒形状以及系统对焦程度对检测结果的干扰。实验结果表明:利用离焦弥散圆检测颗粒尺寸的方法在不同离焦量下都有较高的检测精度,相较于传统的使用暗场散射显微镜的方法,对于不规则形状颗粒尺寸的检测误差从平均58%降低到10.3%。验证了离焦弥散圆检测颗粒尺寸方法的可行性,并可以有效提高检测不规则颗粒尺寸的精度。
Abstract:Optical surface particulate contamination detection is critical to maintaining the imaging performance of space telescopes. Conventional approaches typically employ dark-field scattering microscopy to capture particle images, where particle size is estimated from the circumcircle of the particle’s contour. However, this method requires precise focusing during image acquisition and is prone to large errors when dealing with irregularly shaped particles. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a novel sizing method based on defocus-induced blur circles. By exploiting the relationship between particle size and its scattered light energy, the defocused dark-field scattering image of a particle is transformed into a blur circle, whose properties can be analyzed to determine the actual particle size. Unlike conventional contour-based measurements, the blur-circle approach is inherently less sensitive to particle shape irregularities and system defocus. Experimental validation demonstrates that the proposed method achieves high sizing accuracy across varying defocus distances. Compared with traditional dark-field scattering microscopy, the average measurement error for irregularly shaped particles is significantly reduced—from 58% to 10.3%. These results confirm both the feasibility and effectiveness of the blur circle method in improving measurement precision for irregular particulate contaminants.
-
Key words:
- particle detection /
- dark-field scattering /
- point spread function /
- Mie scattering
-
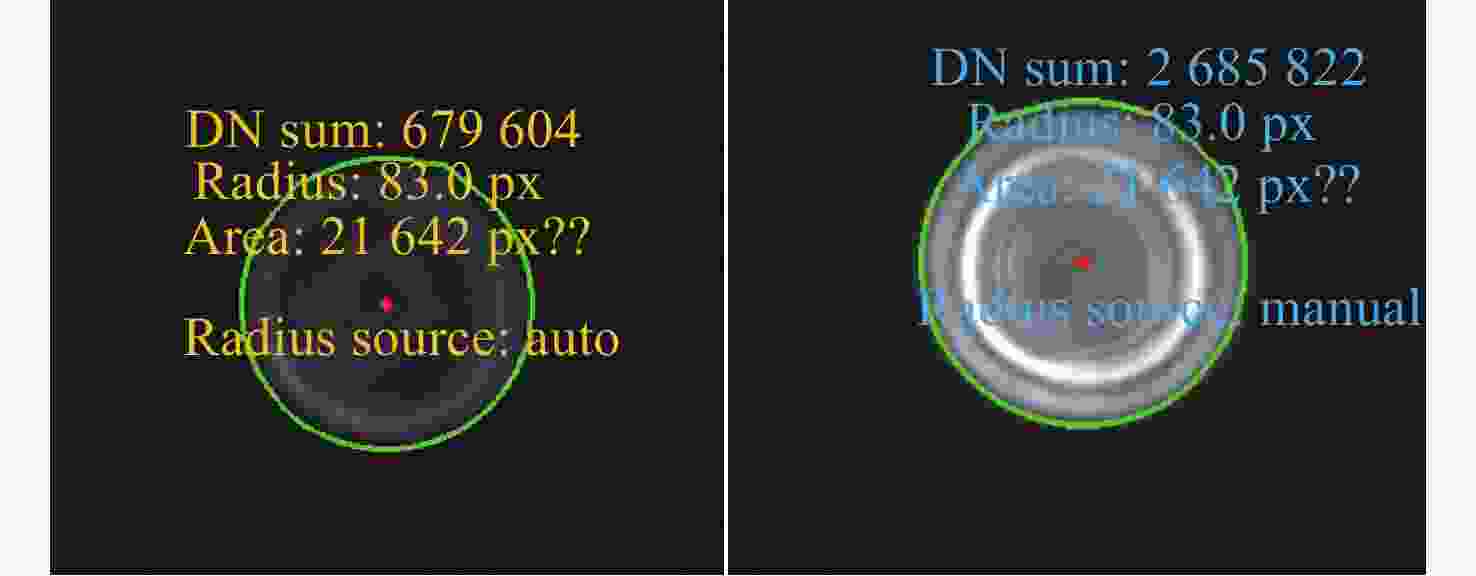
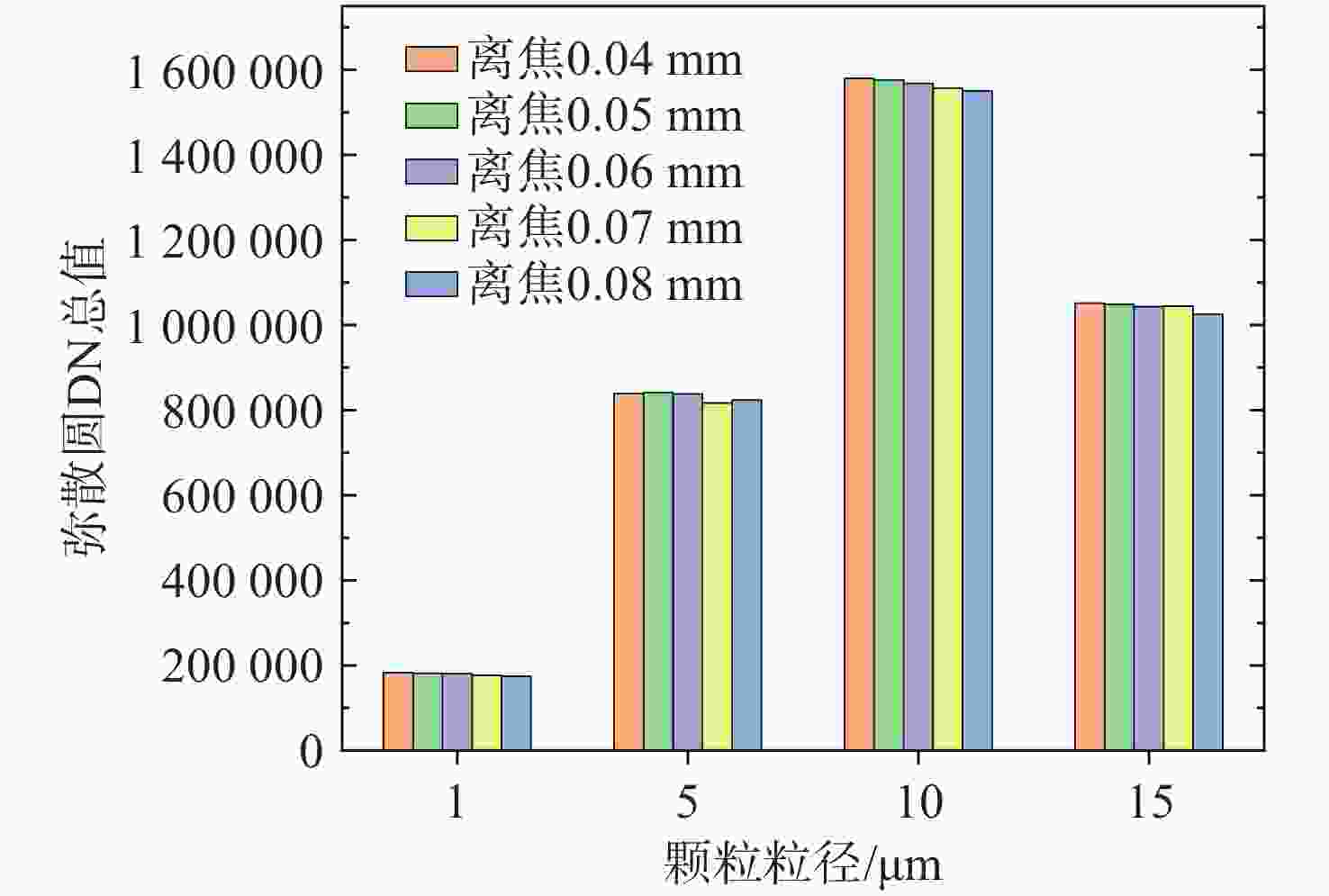
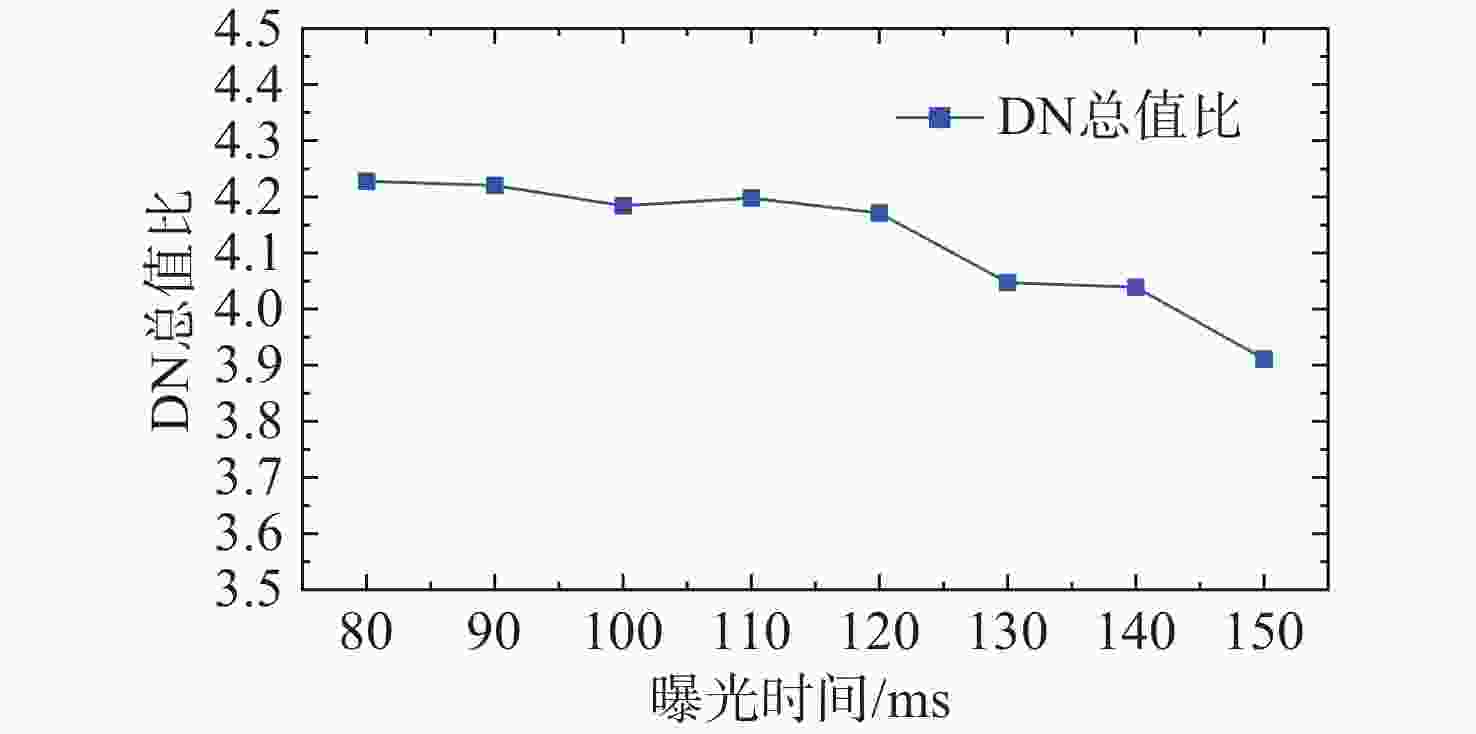
表 1 不同颗粒在不同离焦量下的DN总值差异
Table 1. Differences in total DN values of different particles across various defocus amounts.
颗粒尺寸 最大相对偏差 变异系数 1 μm 4.6% 1.93% 5 μm 2.9% 1.31% 10 μm 2.5% 0.98% 15 μm 2.4% 0.97% 表 2 圆形与不规则颗粒检测结果
Table 2. Round and Irregular Particles Detection Results
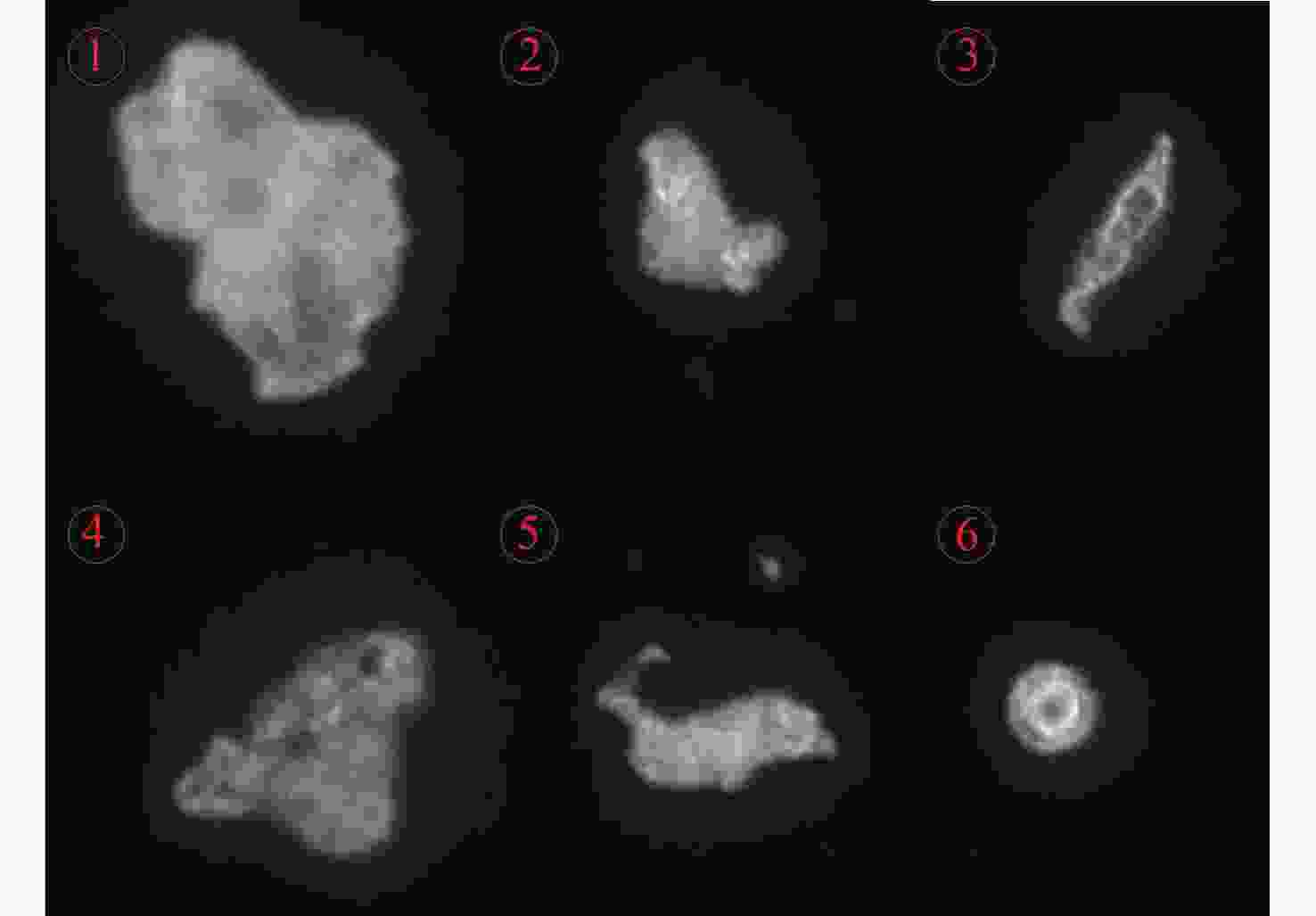
圆形颗粒 不规则颗粒 轮廓像素 732 430 外接圆像素 793 2156 相对误差 4.2% 401.4% 表 3 离焦检测与外接圆算法的误差水平
Table 3. Defocus Detection and Circumcircle Algorithm Error Level
弥散圆方法误差 外接圆方法误差 1 8% 54% 2 0.5% 79% 3 10% 40% 4 20% 54% 5 13% 67% 平均误差水平 10.3% 58% -
[1] 周济林, 谢基伟, 葛健, 等. 空间系外行星探测与研究进展[J]. 空间科学学报, 2024, 44(1): 5-18. doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.01.2024-yg01ZHOU J L, XIE J W, GE J, et al. Progress on exoplanet detection and research in space[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2024, 44(1): 5-18. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11728/cjss2024.01.2024-yg01 [2] WOOLDRIDGE E, ARENBERG J. Contamination effects and requirements derivation for the James Webb Space Telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7069: 70690J. doi: 10.1117/12.801664 [3] WARD J O, JONES C B, GOLDMAN E W. Precious cargo: transporting contamination-sensitive instruments and optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2022, 12224: 1222405. [4] VENKATA S, BUDIHAL R P. Light scattering due to particulate contamination over the primary mirror of Visible Emission Line Coronagraph on board Aditya-L1 mission[J]. Optical Engineering, 2021, 60(7): 074103. [5] 冷荣宽, 王上, 王智, 等. 空间引力波探测前向杂散光测量和抑制[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(5): 1081-1088. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0251LENG R K, WANG SH, WANG ZH, et al. Measurement and suppression of forward stray light for spaceborne gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1081-1088. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0251 [6] 杨星宇. 超光滑表面疵病的显微散射检测方法[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2015.YANG X Y. Microscopic scattering detection for defects on ultra-smooth surfaces[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2015. (in Chinese) . [7] 吴凡. 基于暗场散射的精密表面微小缺陷检测能力提升技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020.WU F. Detection capability improvement technology for weak defects on smooth surfaces based on dark field scattering[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020. (in Chinese). [8] 邓泉, 赵泽宇, 林鹤, 等. 晶圆金属表面纳米颗粒暗场检测系统设计[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 , 2023, 50(22): 2204003. doi: 10.3788/CJL230444DENG Q, ZHAO Z Y, LIN H, et al. System design for dark-field detection of nanoparticles on wafer metal surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(22): 2204003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL230444 [9] 李佳慧, 匡翠方, 徐月暑, 等. 极紫外光学元件全频段面形误差检测与缺陷探测技术研究进展[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2025, 33(17): 2661-2690.LI J H, KUANG C F, XU Y SH, et al. Research progress of full-spatial frequency error measurement and defect detection technology for extreme ultraviolet optical components[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2025, 33(17): 2661-2690. (in Chinese). [10] 刘自轩. 基于机器学习的颗粒光散射信号特征提取与属性识别[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2023.LIU Z X. Feature extraction and attribute recognition of particle light scattering signals based on machine learning[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2023. (in Chinese). [11] 艾立夫. 基于散射光暗场显微的基片表面颗粒检测方法研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院光电技术研究所), 2019.AI L F. The detection method of substrate surface particles based on dark field microscopy of scattered light[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese). [12] 高友帅. 基于光散射成像的单颗粒追踪方法及其在细胞微环境中的应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2024.GAO Y SH. Research on single particle tracking method based on light scattering imaging and its application in cellular microenvironment[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2024. (in Chinese). [13] 贺仁智. 基于离焦图像的深度估计与测量[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2023.HE R ZH. Depth estimation and measurement based on focused images[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2023. (in Chinese). [14] 沈建琪. 光散射法测粒技术延伸测量下限的研究[D]. 上海: 上海理工大学, 1999.SHEN J Q. Extension of lower measurement limit for particle sizing by light scattering[D]. Shanghai: University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 1999. (in Chinese) . [15] DORODNYY A, SMAJIC J, LEUTHOLD J. Mie scattering for photonic devices[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2023, 17(9): 2300055. [16] 曹西乐, 田兴, 穆童. 基于Mie理论和Debye模型的球形粒子散射特性研究[J]. 电子制作, 2025, 33(1): 116-120.CAO X L, TIAN X, MU T. Study on scattering characteristics of spherical particles based on Mie theory and Debye model[J]. Practical Electronics, 2025, 33(1): 116-120. (in Chinese) . [17] NAHM K B, WOLFE W L. Light-scattering models for spheres on a conducting plane: comparison with experiment[J]. Applied Optics, 1987, 26(15): 2995-2999. doi: 10.1364/AO.26.002995 [18] STOKSETH P A. Properties of a defocused optical system[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1969, 59(10): 1314-1321. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.59.001314 -





 下载:
下载: