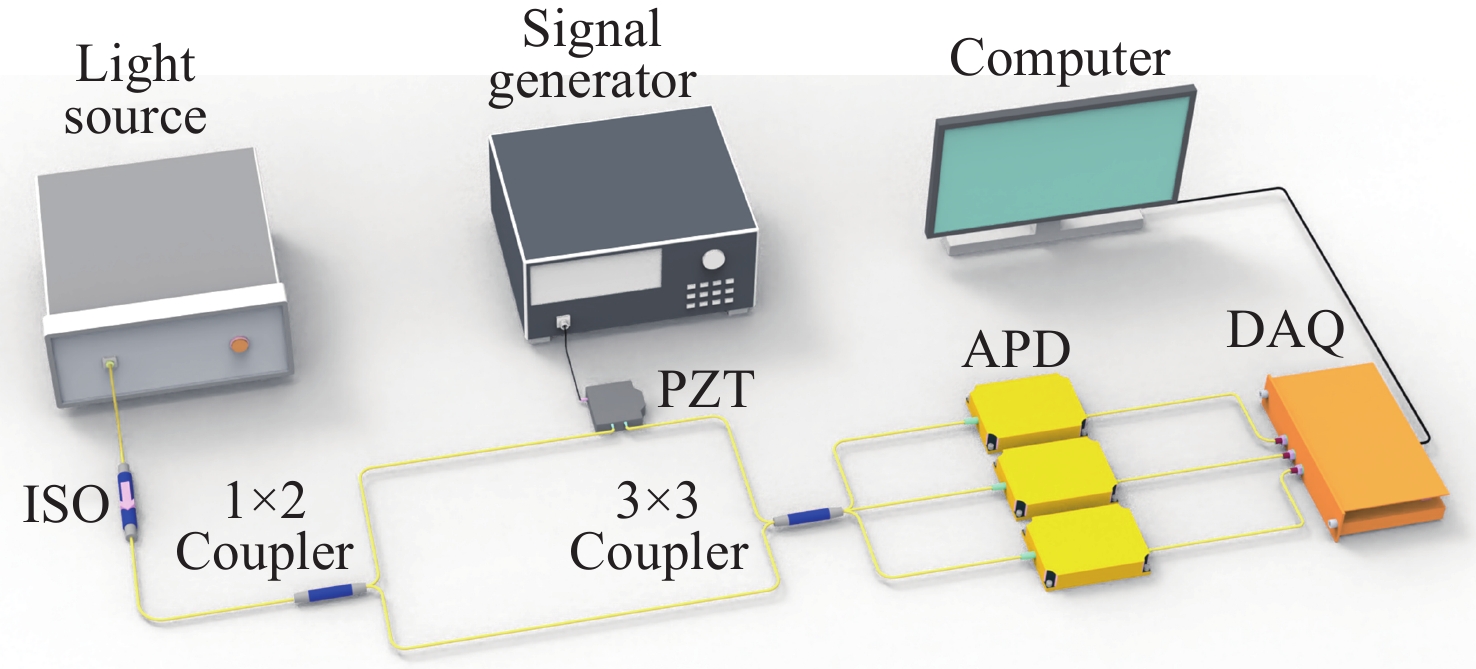
A noise suppression method for interferometric fiber optic sensor based on ameliorated EFA and adaptive SVMD
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0038
-
摘要:
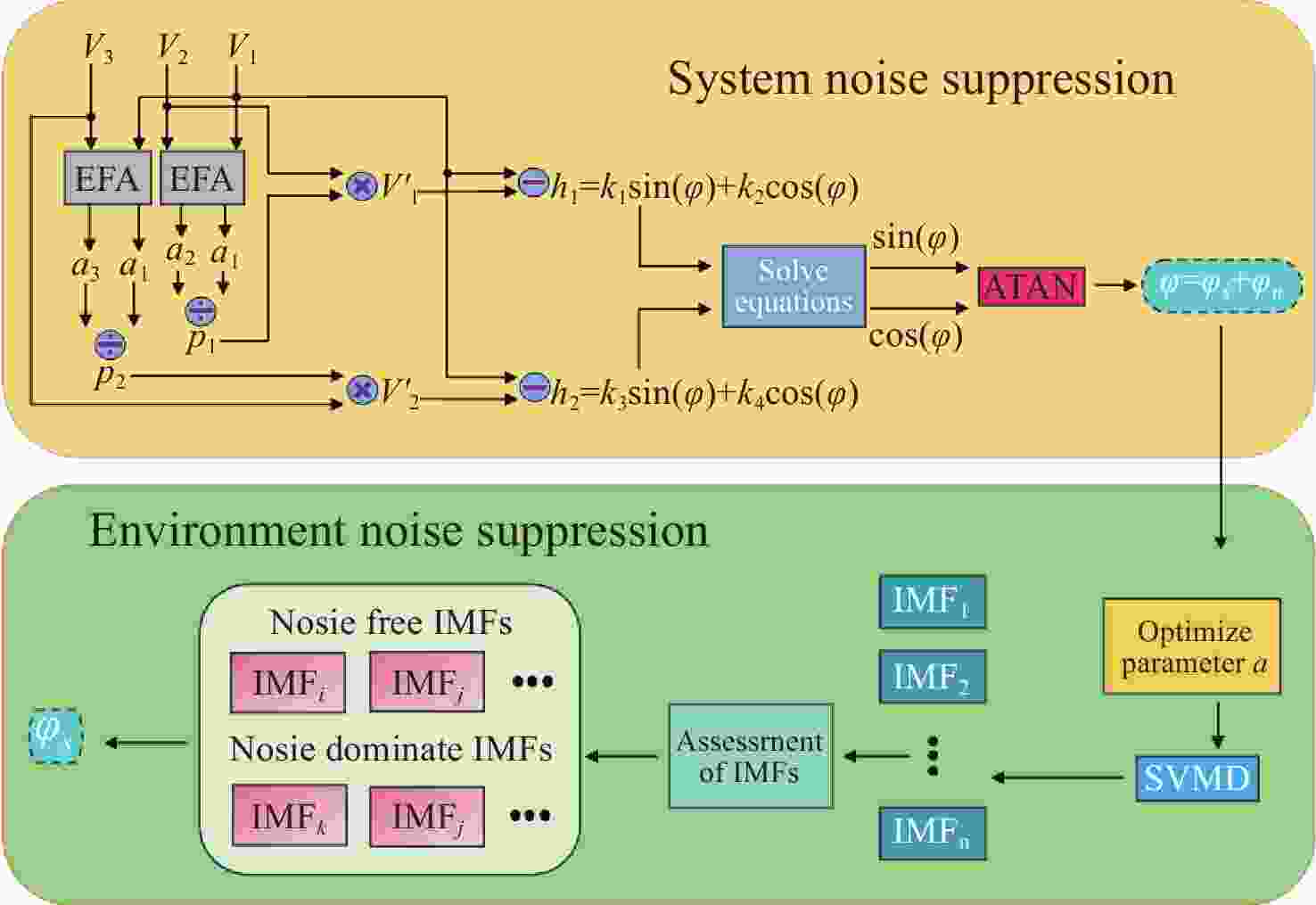
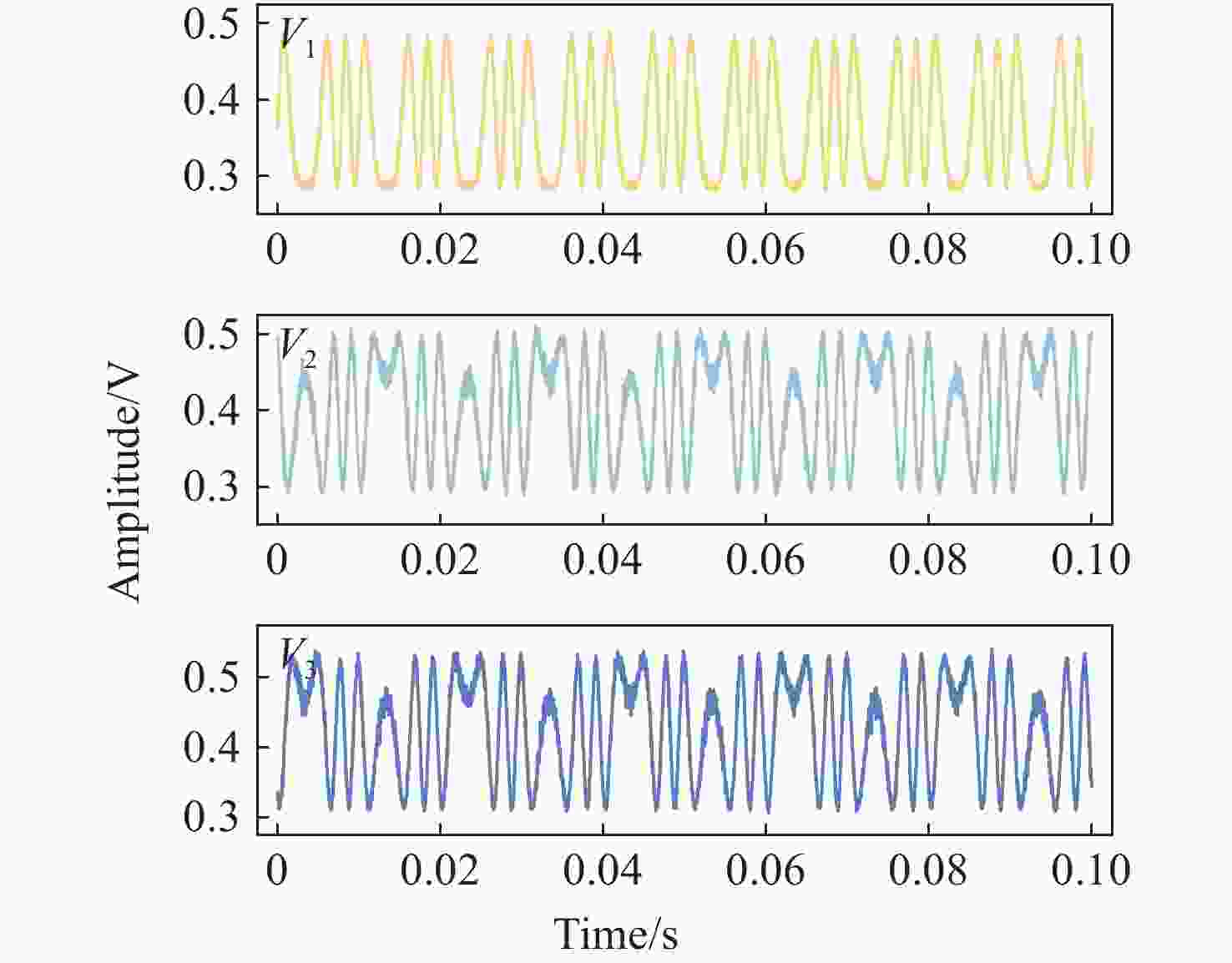
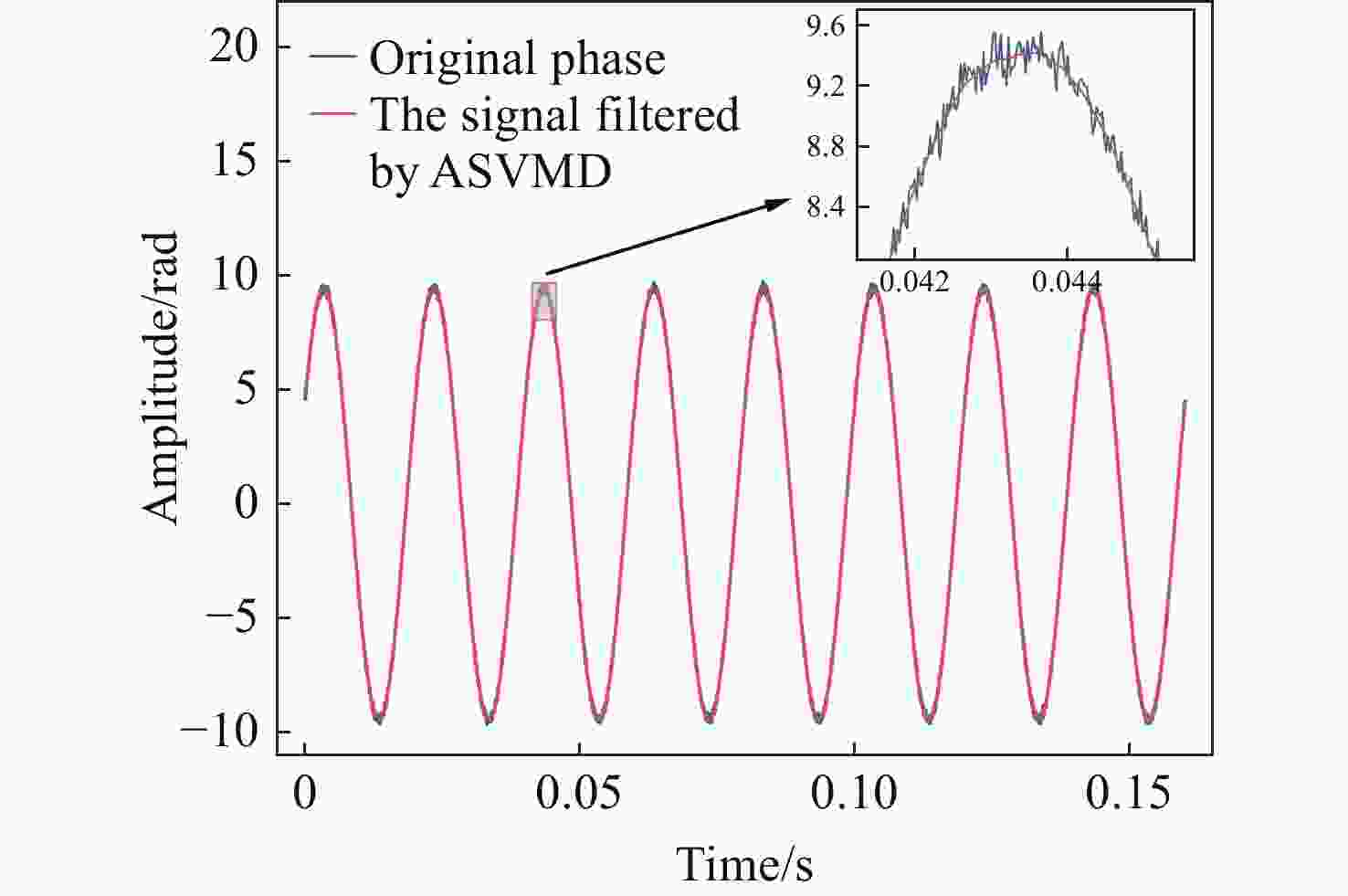
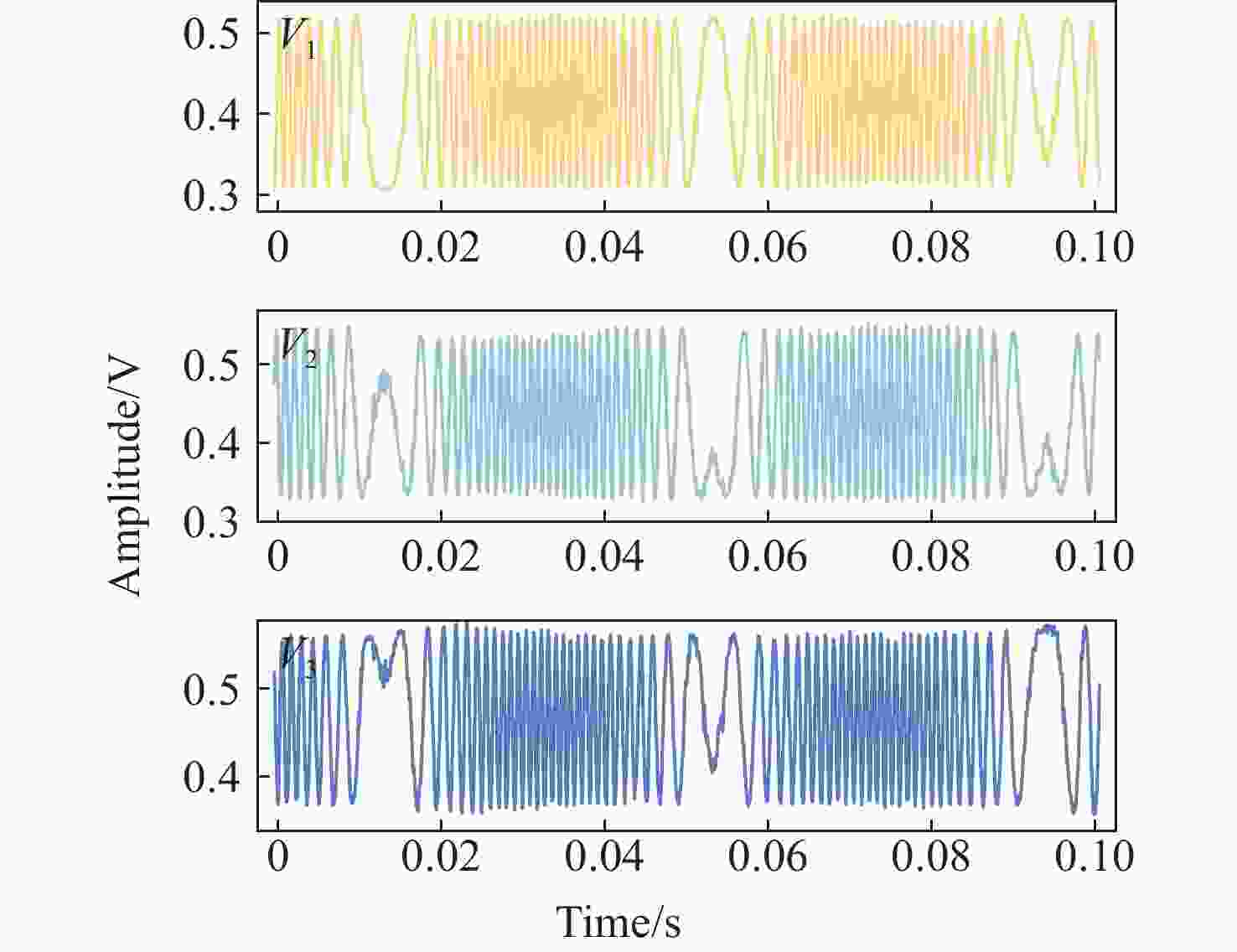
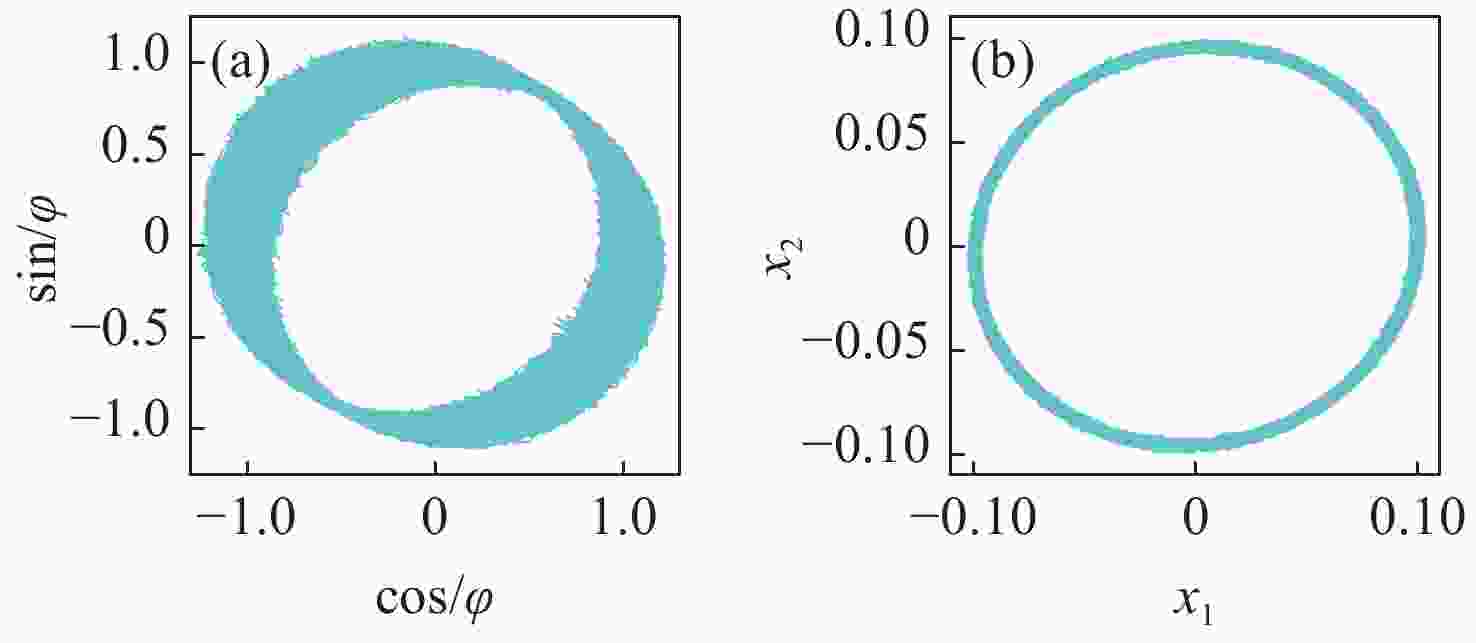
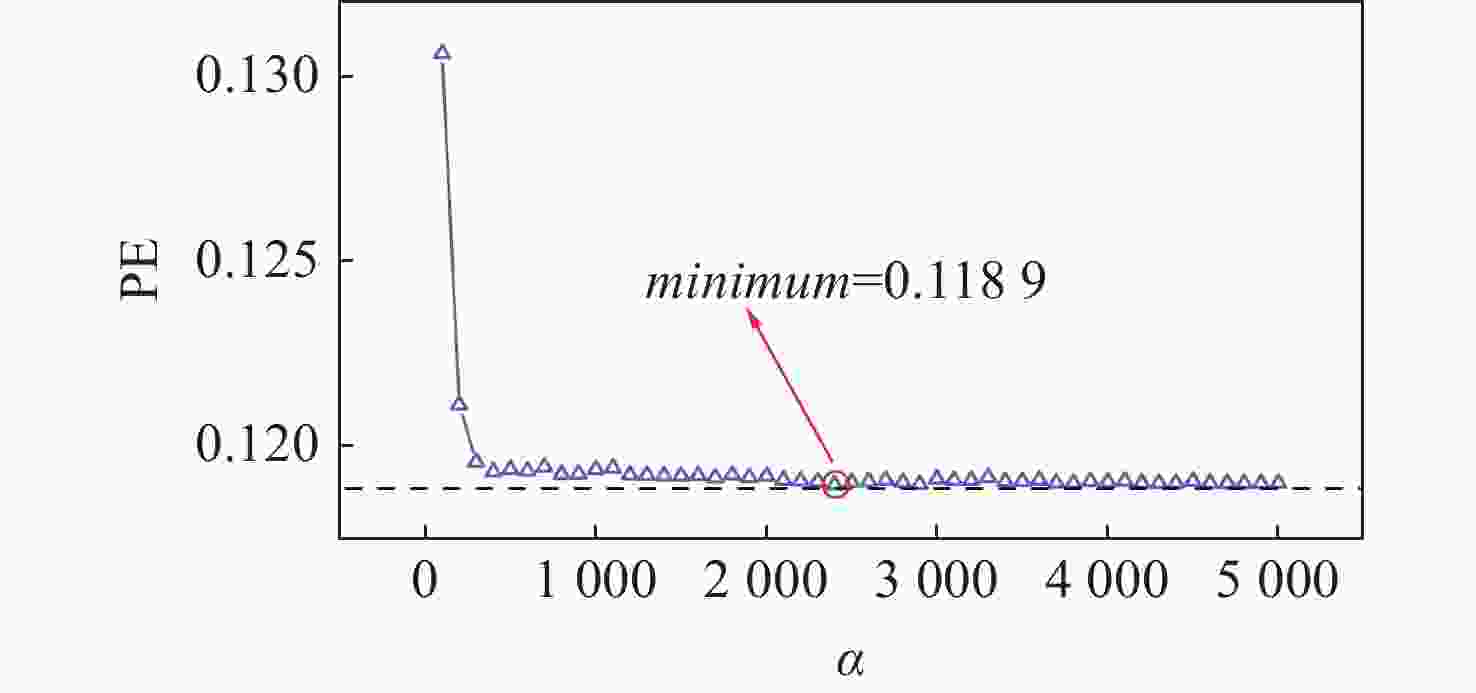
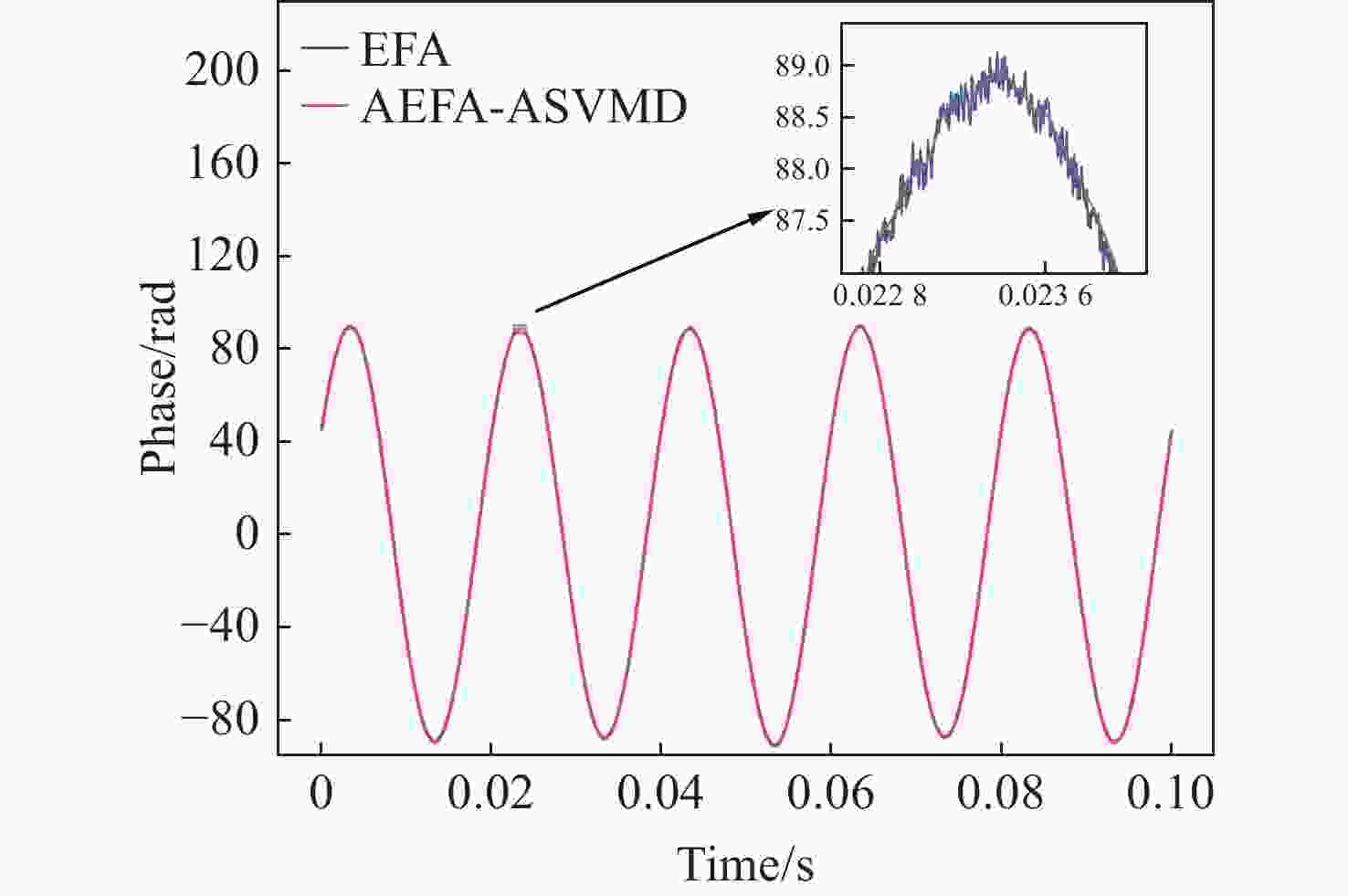
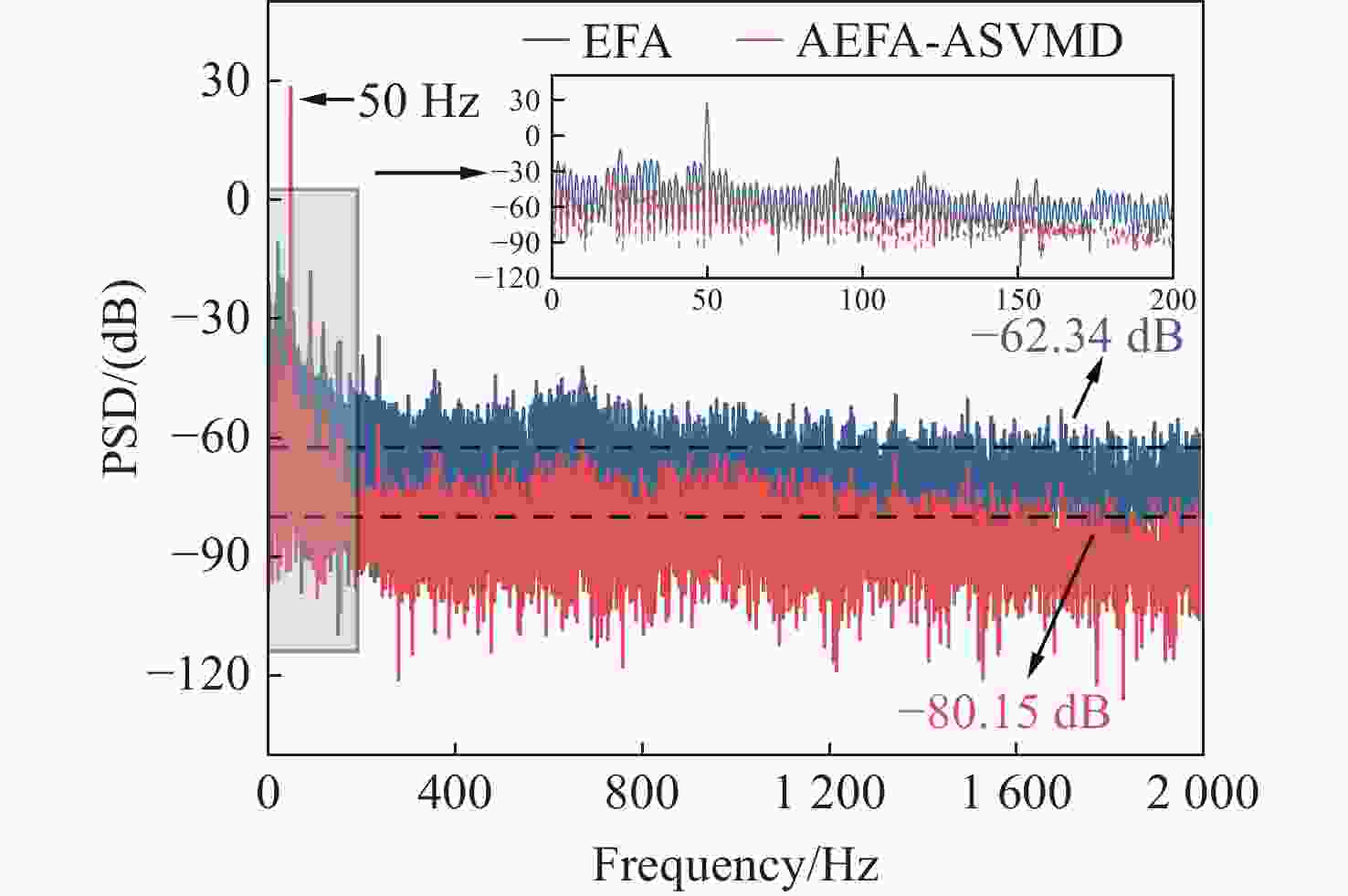
噪声干扰是影响传感系统稳定性和数据准确性的关键瓶颈,现有的抑制策略无法同时降低固有系统噪声和外部环境噪声。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了一种基于改进椭圆拟合算法(AEFA)和自适应连续变分模分解(ASVMD)的复合去噪方法。对于与干涉信号中直流(DC)、交流(AC)分量紧密耦合的系统噪声,AEFA 通过消除上述分量实现有效抑制。主要存在于解调相位信号中的环境噪声分量可以通过SVMD技术自适应地提取。为了自动获得最优分解结果,引入置换熵(PE)准则来优化分解参数。相关系数(CC)用于区分分解结果中的有效分量和噪声分量。实验结果表明,AEFA和ASVMD相结合的算法有效地抑制了系统和环境噪声。在处理50 Hz振动信号时,所提出的方案实现了17.81 dB的降噪和35.14 μrad/√Hz的相位分辨率。鉴于其出色的噪声抑制性能,该方案在高性能干涉传感系统中具有巨大的应用潜力。
-
关键词:
- 干涉型光纤振动传感器 /
- 椭圆拟合算法 /
- 连续变分模分解 /
- 噪声抑制
Abstract:Noise interference is a critical bottleneck that affects the stability of sensing systems and the accuracy of data, and existing suppression strategies are unable to simultaneously reduce both inherent system noise and external environmental noise. To address this problem, this paper proposes a composite denoising method based on ameliorated ellipse fitting algorithm (AEFA) and adaptive successive variational mode decomposition (ASVMD). System noise, which is closely correlated with the direct-current (DC) and alternating-current (AC) components in the interferometric signal, is effectively suppressed in AEFA through the elimination of these components. Environmental noise components, which primarily reside in the demodulated phase signal, can be adaptively extracted by the SVMD technique. In order to automatically obtain the optimal decomposition results, the permutation entropy (PE) criterion is introduced to optimize the decomposition parameters. Correlation coefficient (CC) is used to distinguish between the effective components and noise components in the decomposition results. Experimental results indicate that the combined AEFA and ASVMD algorithm effectively suppresses both system and environmental noise. When applied to 50 Hz vibration signal processing, the proposed scheme achieves noise reduction of 17.81 dB and a phase resolution of 35.14 μrad/√Hz. Given the excellent performance of the noise suppression, the proposed scheme holds great application potential in high-performance interferometric sensing systems.
-
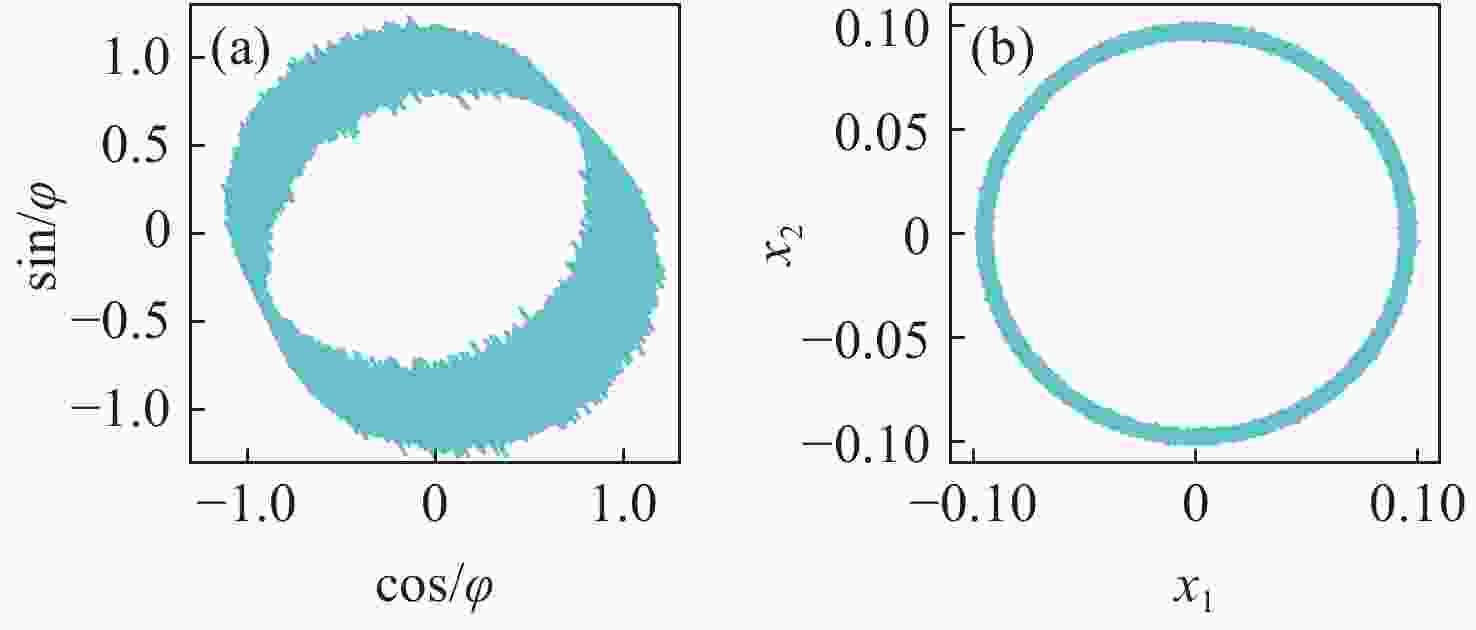
Table 1. Comparison of THD and SNR between EFA and AEFA results
Algorithm THD (%) SNR (dB) EFA 0.1541 37.6787 AEFA 0.1120 40.0029 Table 2. The CC between decomposition results and simulated signal
IMF component CC IMF1 0.9999 IMF2 0.0038 IMF3 0.0036 Table 3. Comparison of THD and SNR between EFA And AEFA results
Algorithm THD (%) SNR (dB) EFA 0.1733 52.9978 AEFA 0.1716 54.2644 Table 4. The CC between decomposition results and experimental signal
IMF component CC value IMF1 0.9999 IMF2 0.0037 IMF3 0.0015 IMF4 0.0007 IMF5 0.0005 IMF6 0.0006 -
[1] MA SH N, XU Y P, PANG Y X, et al. Optical fiber sensors for high-temperature monitoring: a review[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(15): 5722. doi: 10.3390/s22155722 [2] SAHOTA J K, GUPTA N, DHAWAN D. Fiber Bragg grating sensors for monitoring of physical parameters: a comprehensive review[J]. Optical Engineering, 2020, 59(6): 060901. [3] PENDÃO C, SILVA I. Optical fiber sensors and sensing networks: overview of the main principles and applications[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(19): 7554. doi: 10.3390/s22197554 [4] GUEVARA-HERNANDEZ S D, HERNANDEZ-GARCIA J C, FILOTEO-RAZO J D, et al. Design and study of fiber optic interferometric devices applied to vibration detection systems[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2024, 12880: 1288005. [5] CORREA A I, GALARZA M, DAULIAT R, et al. High-frequency vibration sensor using a fiber laser with a multicore fiber interferometer[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(6): 7656-7662. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3348502 [6] ALSHAMMARI M, CHU Y F, HAN M. Real-time in situ phase sensitivity calibration of interferometric fiber-optic ultrasonic sensors[J]. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(18): 5336-5339. doi: 10.1364/OL.538136 [7] HE Z Y, LIU Q W. Optical fiber distributed acoustic sensors: a review[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(12): 3671-3686. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2021.3059771 [8] PLOTNIKOV M Y, LAVROV V S, DMITRASCHENKO P Y, et al. Thin cable fiber-optic hydrophone array for passive acoustic surveillance applications[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(9): 3376-3382. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2894323 [9] TEJEDOR J, MACIAS-GUARASA J, MARTINS H F, et al. Real field deployment of a smart fiber-optic surveillance system for pipeline integrity threat detection: architectural issues and blind field test results[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2018, 36(4): 1052-1062. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2780126 [10] PAN ZH, LIU H J, WANG L X, et al. Draw-tower-grating-based Fabry-Perot interferometers for simultaneous measurements of temperature and salinity[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(13): 22687-22699. doi: 10.1364/OE.523935 [11] KIRKENDALL C K, DANDRIDGE A. Overview of high performance fibre-optic sensing[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2004, 37(18): R197-R216. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/37/18/R01 [12] LIU F, XIE SH R, GU L J, et al. Common-mode noise suppression technique in interferometric fiber-optic sensors[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2019, 37(21): 5619-5627. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2019.2933449 [13] PAN ZH, XU B, CHEN W J, et al. Improved complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise and its application in noise reduction for fiber optic sensing[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2025, 43(5): 2466-2474. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2024.3489953 [14] GUI L, WU X Q, YU B L, et al. An improved PGC demodulation algorithm based on a reference interferometer to reduce intensity and phase noise[J]. Optik, 2021, 247: 167884. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167884 [15] ZHANG SH, ZHANG A L, PAN H G. Eliminating light intensity disturbance with reference compensation in interferometers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2015, 27(17): 1888-1891. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2015.2444421 [16] XIA Q L, WU X Q, LIU X P, et al. Common-mode intensity noise suppression scheme in phase demodulation of 3×3 coupler based on ellipse fitting algorithm[J]. Optics Communications, 2025, 575: 131291. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2024.131291 [17] YU ZH H, CAI Y F, MO D L. Comparative study on noise reduction effect of fiber optic hydrophone based on LMS and NLMS algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(1): 301. doi: 10.3390/s20010301 [18] LIU H J, ZHOU C M, PANG Y D, et al. Novel method for improving temperature resolution of fiber optic sensor based on variational mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(6): 2137-2143. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3325255 [19] PAN ZH, LIU H J, WANG L X, et al. A novel method for improving salinity resolution of optical fiber sensor based on modified adaptive variational mode decomposition[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2024, 177: 111212. [20] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K, ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531-544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [21] MISHRA S P, WARULE P, DEB S. Speech emotion recognition using a combination of variational mode decomposition and Hilbert transform[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2024, 222: 110046. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2024.110046 [22] LI D Q, YI D, FU W Q, et al. Temperature and acoustic field reconstruction in fiber optic DAS system based on variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(10): 16196-16203. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3385206 [23] NASSEF M G A, HUSSEIN T M, MOKHIAMAR O. An adaptive variational mode decomposition based on sailfish optimization algorithm and Gini index for fault identification in rolling bearings[J]. Measurement, 2021, 173: 108514. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108514 [24] RAYI V K, MISHRA S P, NAIK J, et al. Adaptive VMD based optimized deep learning mixed kernel ELM autoencoder for single and multistep wind power forecasting[J]. Energy, 2022, 244: 122585. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.122585 [25] NAZARI M, SAKHAEI S M. Successive variational mode decomposition[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 174: 107610. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107610 [26] FANG CH X, SHI J H, FU ZH Y, et al. Improved ellipse-fitting phase demodulation technique to suppress the effect of light source intensity noise in interferometric system[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(7): 1690-1693. doi: 10.1364/OL.483090 [27] GUO Y J, YANG Y D, JIANG SH F, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on successive variational mode decomposition and the EP index[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(10): 3889. doi: 10.3390/s22103889 [28] BANDT C, POMPE B. Permutation entropy: a natural complexity measure for time series[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 88(17): 174102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.174102 -





 下载:
下载: