-
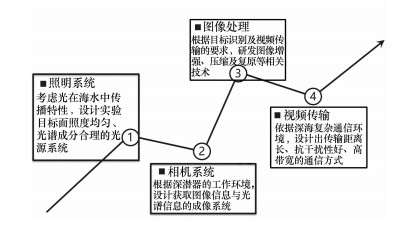
摘要: 深海光学成像系统分为4个子系统:照明系统、相机系统、图像处理系统以及数据存储与传输系统,本文对深海光学成像系统化研究与发展趋势展开分析。文中有针对性地对深海光学成像最前端的两个子系统-照明系统与相机系统进行了较为详细地阐述。其中,深海照明系统进一步细分为3个更小的系统:光源系统、配光系统以及灯阵系统;对于深海相机系统则根据其应用领域及技术特点细分为水下普通成像、金宝搏188软件怎么用 成像、偏振光成像、3D/全景成像、显微成像以及光谱成像6类。从近年来国内外深海光学成像的发展历史及现状来看,其未来的发展趋势可以归结为以下几点:更高的分辨率,更深的工作深度,更大的观测范围以及更多样的成像方式。Abstract: The deep-sea optical imaging system is divided into four subsystems:illumination system, camera system, image processing system and data storage and transmission system. On the basis of above, a systematic study and development trend analysis of deep-sea optical imaging is conducted in this paper. Then, the two sub-systems of the forefront of deep-sea optical imaging, illumination system and camera system, are described in detail. Among them, the deep-sea illumination system is further subdivided into three smaller systems:light source system, light distribution system and lamp array system; and for the deep-sea camera system, according to its application areas and technical characteristics, it can be subdivided into 6 categories, namely, normal imaging, laser imaging, polarized light imaging, 3D/panoramic imaging, microscopic imaging and spectral imaging. Based on the history and current situation of deep-sea optical imaging both at home and abroad in recent years, its future development trend can be summarized as follows:higher resolution, deeper working depth, larger observation range and more diverse imaging method.
-
Key words:
- deep-sea optics /
- deep-sea lighting system /
- deep-sea camera system /
-
图 5 金宝搏188软件怎么用 成像距离示意图:(a)普通成像方式,照明灯与摄像机在同一位置,散射光最多;(b)改进的普通成像,照明角度与成像角度成一定夹角,照明区域与成像区域重叠部分变小,后向散射光也同时减少;(c)和(d)则采用金宝搏188软件怎么用 照明,散射光得到很好的抑制,成像距离最大达到6个衰减长度
Figure 5. Sketch diagram of laser imaging distance. (a)Usual imaging:the lamp and camera are fixed in the same place; (b)the advanced imaging:the lamp and camera are fixed in different place and the overlap area of illumination and imaging is smaller. So the scattering light is decreased. (c) and (d)Laser illumination:the scattering light is decreased to a great extent. The work distance is about 6 attenuation length
图 11 3D/全景相机代表产品:(a)所示为卡梅隆拍摄影片时乘坐的深渊挑战者号载人潜器,上面搭载了其团队和Scripps海洋研究所共同研制的3D相机;(b)是WHOI研制的3D深海深海相机;(c)是俄罗斯公司研制的水下全景相机,工作深度为200 m;(d)是美国公司研制的水下全景相机,工作深度为2 000 m
Figure 11. Representative products of 3D/Panorama camera:(a)3D camera of "Challenger " manned submersible which is manufactured by Scripps; (b)deep-sea 3D camera system of WHOI; (c)underwater panorama camera of Russia, working depth is 200 m; (d)underwater panorama camera of America, working depth is 2 000 m
表 1 国内外典型深海光学相机设备性能
Table 1. Performances of the most developed deep-sea cameras in the world
厂家 视场角/(°) 分辨率/(p) 工作深度/km 变焦比 灵敏度/lx 备注 Kongsberg 230 1 080 6 000 36:1 1×10-6 Deep-sea power & light 185 1 080 11 000 30:1 4.5×10-4 Sub C 142 2 160 11 000 20:1 0.02 通过光纤可传4K视频 西光所 / 1 080 11 000 / / 自容式 上海恒生 80 1 080 7 000 / 可调 -
[1] JAFFE J S. To sea and to see:that is the answer[J]. Methods in Oceanography, 2016, 15:3-20. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211122016300238 [2] ARNAUBEC A, OPDERBECKE J, ALLAIS A G, et al. . Optical Mapping with the ARIANE HROV at IFREMER: the matisse processing Tool[C]. OCEANS 2015, IEEE, 2015: 1-6. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/308825792_Optical_mapping_with_the_ARIANE_HROV_at_IFREMER_The_MATISSE_processing_tool [3] KWASNITSCHKA T, KÖSER K, STICKLUS J, et al.. DeepSurveyCam-a deep ocean optical mapping system[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(2), Doi:10.33901s16020164. [4] 孙传东, 李驰, 张建华, 等.水下成像镜头的光学设计[J].光学精密工程, 1998, 6(5):5-11. http://www.eope.net/fileup/PDF/19980502.pdfSUN CH D, LI CH, ZHANG J H, et al.. Optical design of the lens for underwater imaging system[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 1998, 6(5):5-11.(in Chinese) http://www.eope.net/fileup/PDF/19980502.pdf [5] Imaging Marine Life: Macrophotography and Microscopy Approaches for Marine Biology[M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2013. [6] WANG B, SOCOLOFSKY S A. A deep-sea, high-speed, stereoscopic imaging system for in situ measurement of natural seep bubble and droplet characteristics[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2015, 104:134-148. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2015.08.001 [7] JAFFE J S. Underwater optical imaging:the past, the present, and the prospects[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2015, 40(3):683-700. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2014.2350751 [8] CHEN J, ZHANG Q, ZHANG A, et al. . 7000M lander design for hadal research[C]. OCEANS 2014, IEEE, 2014: 1-4. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/281687657_7000M_lander_design_for_hadal_research [9] KOCAK D M, CAIMI F M. The current art of underwater imaging-with a glimpse of the past and vision of the future[J]. Marine Technology Society Journal, 2005, 39(3):5-26. doi: 10.4031/002533205787442576 [10] 郑玉权, 王慧, 王一凡.星载高光谱成像仪光学系统的选择与设计[J].光学精密工程, 2009, 17(11):2629-2637. http://www.eope.net/fileup/PDF/2008-0918.pdfZHENG Y Q, WANG H, WANG Y F. Selection and design of optical systems for spaceborne hyperspectral imagers[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2009, 17(11):2629-2637.(inChinese) http://www.eope.net/fileup/PDF/2008-0918.pdf [11] ROSTON J, BRADLEY C, COOPERSTOCK J R. Underwater window: high definition video on VENUS and NEPTUNE[C]. OCEANS 2007, IEEE, 2007: 1-8. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/224305670_underwater_window_high_definition_video_on_venus_and_neptune [12] PARIS C B, ATEMA J, IRISSON J O, et al.. Reef odor:a wake up call for navigation in reef fish larvae[J]. PloS One, 2013, 8(8):e72808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072808 [13] Deepsea Corporation, http://www.deepsea.com/[EB/OL]. San Diego, California. [14] SINGH H, CAN A, EUSTICE R, et al.. Seabed AUV offers new platform for high-resolution imaging[J]. EOS, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2004, 85(31):289-296. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/245586190_SeaBED_AUV_offers_new_platform_for_high-resolution_imaging [15] CAIMI F M, KOCAK D M, DALGLEISH F, et al. . Underwater imaging and optics: recent advances[C]. OCEANS 2008, IEEE, 2008: 1-9. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/224605203_Underwater_imaging_and_optics_Recent_advances [16] SAHU P, GUPTA N, SHARMA N. A survey on underwater image enhancement techniques[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2014, 87(13):19-23. doi: 10.5120/15268-3743 [17] LU H, LI Y, SERIKAWA S, et al. . Image restoration method for deep-sea tripod observation systems in the South China Sea[C]. MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2015, IEEE, 2015: 1-6. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/315928925_Image_restoration_method_for_deep-sea_tripod_observation_systems_in_the_South_China_Sea [18] 郑峰, 刘丽莹, 刘小溪, 等.多主色LED照明光源的相关色温调控[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(4):926-933. http://www.opticsjournal.net/Abstract.htm?id=OJ150520000143oVrXu1ZHENG F, LIU L Y, LIU X X, et al.. Control of correlated color temperature for multi-primary color LED illumination[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2015, 23(4):926-933.(in Chinese) http://www.opticsjournal.net/Abstract.htm?id=OJ150520000143oVrXu1 [19] 苏方雨.深海用水下照明灯具[J].海洋渔业, 1990, 1:39-42. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93342X/1990001/271550.htmlSUN F Y. Lighting lamps in deep-sea[J]. Marine Fisheries, 1990, 1:39-42.(in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93342X/1990001/271550.html [20] KAWAKAMI, TAKASHI SATO, TOMOO USAMI, Sachiko submersible illumination device: JP, 2002100203[P]. 2002-04-05. [21] CHANG P C Y, FLITTON J C, HOPCRAFT K I, et al. Improving visibility depth in passive underwater imaging by use of polarization[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(15):2794-2803. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.002794 [22] WIDDER E A, ROBISON B H, REISENBICHLER K R, et al.. Using red light for in situ observations of deep-sea fishes[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2005, 52(11):2077-2085. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2005.06.007 [23] HARDY K R, OLSSON M S, SANDERSON J R, et al. . High brightness light emitting diodes for ocean applications[C]. OCEANS 2007, IEEE, 2007: 1-4. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/224305727_High_Brightness_Light_Emitting_Diodes_for_Ocean_Applications [24] JAFFE J S. Enhanced extended range underwater imaging via structured illumination[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(12):12328-12340. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.012328 [25] 楼志斌.半导体照明技术在水下探测设备中的应用研究[J].船舶工程, 2011, 33(6):96-99. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_cbgc201106025LOU ZH B. Application of semiconductor lighting technology in underwater detection equipment[J]. Ship Engineering, 2011, 33(6):96-99.(in Chinese) http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_cbgc201106025 [26] OLSSON M S. Submersible multi-color LED illumination system: US, 8172434[P]. 2012-05-08. [27] 聂瑛, 何志毅.不同波长光源照明的水下成像及光学图像实时处理[J].光学学报, 2014, 34(7):59-65. http://jz.docin.com/p-1544637296.htmlNIE Y, HE ZH Y. Underwater imaging and real-time optical image processing under illumination by light sources with different wavelengths[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34(7):59-65.(in Chinese) http://jz.docin.com/p-1544637296.html [28] CONOVER G, POTUCEK K L, SLONIM L, et al. . Programmable underwater lighting system: US, 9084314[P]. 2015-07-14. [29] OH, LEE S W, MOON J. Underwater multispectral image acquisition system using multi-wavelength light source: KR, 2015/006769[P]. 2016-05-12. [30] 赵会富, 刘华, 孙强, 等.基于折射/全反射/反射/折射结构的准直系统的设计[J].光学精密工程, 2011, 19(7):1472-1479. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ1108150000453y6B9EZHAO H F, LIU H, SUN Q, et al.. Design of RIXR LED collimatine system[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2011, 19(7):1472-1479.(in Chinese) http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ1108150000453y6B9E [31] 冯奇斌, 李亚妮, 李其功, 等.基于发光二极管配光曲线设计自由曲面透镜[J].光学精密工程, 2016, 24(8):1884-1893. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gxjm201608009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQFENG Q B, LI Y N, LI Q G, et al.. Design of double freeform surface lens based on LED radiation characteristics[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2016, 24(8):1884-1893.(in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gxjm201608009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [32] OLSSON M S, PARKER S B, RIMER D G. Deep submersible light assembly with dry pressure dome: US, 4996635[P]. 1991-02-26. [33] 朱海荣, 朱海, 刘金涛, 等.水下航行器光学隐蔽深度测量系统[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(10):2778-2784. http://www.eope.net/gxjmgc/article/2015/2015-10-2778.htmZHU H R, ZHU H, LIU J T, et al.. Measurement system optical concealment depth of underwater vehicle[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2015, 23(10):2778-2784.(in Chinese) http://www.eope.net/gxjmgc/article/2015/2015-10-2778.htm [34] 郭太良, 周雄图, 陈恩果, 等.用于集成成像的针孔/微透镜组合阵列设计与仿真[J].液晶与显示, 2013, 28(6):855-859. http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ140102000306cJfMiOGUO T L, ZHOU X T, CHEN E G, et al.. Design and simulation of combined pinholes/microlens array for integral imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2013, 28(6):855-859.(in Chinese) http://www.opticsjournal.net/abstract.htm?id=OJ140102000306cJfMiO [35] ZHENG B, ZHENG H, ZHAO L F, et al. . Underwater 3D target positioning by inhomogeneous illumination based on binocular stereo vision[C]. MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2012, IEEE, 2012: 1-4. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/261041155_Underwater_3D_target_positioning_by_inhomogeneous_illumination_based_on_binocular_stereo_vision [36] BURKE J. Light conduit underwater illumination system: US, 20160114868[P]. 2016-04-28. [37] 薛庆生, 陈伟.改进的宽谱段车尔尼-特纳光谱成像系统设计[J].光学精密工程, 2012, 20(2):233-240. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc201202004XUE Q SH, CHEN W. Design of modified Czerny-Turner spectral imaging system with wide spectral region[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2012, 20(2):233-240.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxjmgc201202004 [38] 全向前, 阳宁, 陈祥子, 等. 一种基于非均匀场的深海照明方法及系统: CN, 106793428A[P]. 2017-05-31.QUAN X Q, YANG N, CHEN X Z, et al. . A method and system of deep-sea lighting based on non-uniform field: CN, 106793428A[P]. 2017-05-31. (in Chinese) [39] 孙传东, 陈良益, 高立民, 等.水的光学特性及其对水下成像的影响[J].应用光学, 2000, 21(4):39-46. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_yygx200004010.aspxSUN CH D, CHEN L Y, GAO L M, et al.. Water optical properties and their effect on underwater imaging[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2000, 21(4):39-46.(in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_yygx200004010.aspx [40] 熊志奇.深海区光学成像系统的设计和应用[J].水雷战与舰船防护, 2003, 3:33-38. http://www.opticsjournal.net/Journals/lop.htm?action=post&oid=PT180309000157jPmSpXIONG ZH Q. The design and application of optical imaging system in deep sea area[J]. Mine Warfare & Ship Self-defence, 2003, 3:33-38.(in Chinese) http://www.opticsjournal.net/Journals/lop.htm?action=post&oid=PT180309000157jPmSp [41] GORMAN G A. Field deployable dynamic lighting system for turbid water imaging[D]. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2011. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/267370659_FIELD_DEPLOYABLE_DYNAMIC_LIGHTING_SYSTEM_FOR_TURBID_WATER_IMAGING [42] 石晟玮, 王江安, 蒋兴舟, 等.海水衰减系数的多角度后向散射测量技术研究[J].金宝搏188软件怎么用 与红外, 2008, 38(5):417-420. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgyhw200805003SHI SH W, WANG J A, JIANG X ZH, et al.. A new measurement study of attenuation coefficient using multi-angle backscattering signals[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2008, 38(5):417-420.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jgyhw200805003 [43] 黄有为, 金伟其, 丁琨, 等.基于光束空间展宽的水下前向散射成像模型[J].红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程, 2009, 38(4):669-673. http://www.airitilibrary.com/Publication/alDetailPrint?DocID=10072276-200908-200911110003-200911110003-669-673%2b701HUANG Y W, JING W Q, DING K, et al.. Underwater forward scattering imaging model based on beam spatial broadening[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2009, 38(4):669-673.(in Chinese) http://www.airitilibrary.com/Publication/alDetailPrint?DocID=10072276-200908-200911110003-200911110003-669-673%2b701 [44] 沈凌敏, 张琦, 何俊华, 等.水下微光高速摄像照明技术的研究与应用[J].微计算机信息, 2010, 26(1):111-112, 143. http://www.doc88.com/p-801812474550.htmlSHEN L M, ZHANG Q, HE J H, et al.. Research and application of illumination for underwater low-light-level high-speed photograph system[J]. Microcomputer Information, 2010, 26(1):111-112, 143.(in Chinese) http://www.doc88.com/p-801812474550.html [45] 张法全, 王国富, 叶金才, 等.水下光学监控系统照明方式的研究[J].光子学报, 2011, 40(7):1061-1065. https://core.ac.uk/display/71622461ZHANG F Q, WANG G F, YE J C, et al.. Lighting pattern of underwater optical monitoring system[J]. Acta Photonic Sinica, 2011, 40(7):1061-1065.(in Chinese) https://core.ac.uk/display/71622461 [46] 赵欣慰, 金韬, 池灏, 等.不同光照条件下水下成像背景光的建模与研究[J].物理学报, 2015, 64(10):104201. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.104201ZHAO X W, JIN T, CHI H, et al.. Modeling and simulation of the background light in underwater imaging under different illumination conditions[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(10):104201.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.64.104201 [47] TAN C S, SEET G, SLUZEK A, et al.. A novel application of range-gated underwater laser imaging system(ULIS) in near-target turbid medium[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2005, 43(9):995-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2004.10.005 [48] HUANG Y W, CAO F M, JIN W Q, et al.. Underwater pulsed laser range-gated imaging model and its effect on image degradation and restoration[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53(6):061608. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.53.6.061608.full [49] DALGLEISH F R, CAIMI F M, BRITTON W B, et al. . An AUV-deployable pulsed laser line scan(PLLS) imaging sensor[C]. OCEANS 2007, IEEE, 2007: 1-5. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/4318200_An_AUV-deployable_pulsed_laser_line_scan_(PLLS)_imaging_sensor [50] 徐正平, 沈宏海, 姚园, 等.直接测距型无扫描金宝搏188软件怎么用 主动成像验证系统[J].光学精密工程, 2016, 24(2):251-259. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_gxjmgc201602002XU ZH P, SHEN H H, YAO Y, et al.. Scannerless laser active imaging validating system by directly ranging[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2016, 24(2):251-259.(in Chinese) http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_gxjmgc201602002 [51] 李灿, 宋淑梅, 刘英, 等.折反式眼底相机光学系统设计[J].光学精密工程, 2012, 20(8):1710-1717. http://www.eope.net/gxjmgc/CN/abstract/abstract11029.shtmlLI C, SONG SH M, LIU Y, et al.. Design of optical system for catadioptric fundus camera[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2012, 20(8):1710-1717.(in Chinese) http://www.eope.net/gxjmgc/CN/abstract/abstract11029.shtml [52] MacDONALD I R, REILLY F F, BLINCOW M, et al. . Deep-ocean use of the sm2000 laser line scanner on submarine NR-1 demonstrates system potential for industry and basic science[C]. MTS/IEEE OCEANS 1995, IEEE, 1995: 555-565. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/3666436_Deep-ocean_use_of_the_SM2000_laser_line_scanner_on_submarine_NR-1_demonstrates_system_potential_for_industry_and_basic_science [53] MINOR L G. Dual mode semi-active laser/laser radar seeker: US, 6262800[P]. 2001-07-17. [54] JAFFE J S. Development of a laser line scan lidar imaging system for auv use[R]. Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla CA, 2010. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/235191354_Development_of_a_Laser_Line_Scan_LIDAR_Imaging_System_for_AUV_Use [55] 沈凌云, 郎百和, 朱明, 等.数字直接制版系统的金宝搏188软件怎么用 扫描成像设计[J].液晶与显示, 2012, 27(5):687-691. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDDJ201610011.htmSHEN L Y, LANG B H, ZHU M, et al.. Design of laser scanning imaging for digital computer-to-plate system[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2012, 27(5):687-691.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDDJ201610011.htm [56] SHASHAR N, SABBAH S, CRONIN T W. Transmission of linearly polarized light in seawater:implications for polarization signaling[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2004, 207(20):3619-3628. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01187 [57] CRONIN T W, SHASHAR N, CALDWELL R L, et al.. Polarization vision and its role in biological signaling[J]. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 2003, 43(4):549-558. doi: 10.1093/icb/43.4.549 [58] TREIBITZ T, SCHECHNER Y Y. Active polarization descattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(3):385-399. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.85 [59] MASSOT-CAMPOS M, OLIVER-CODINA G. Optical sensors and methods for underwater 3D reconstruction[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(12):31525-31557. doi: 10.3390/s151229864 [60] HARDY K, BULMAN T, CAMERON J, et al. . Hadal landers: the DEEPSEA CHALLENGE ocean trench free vehicles[C]. MTS/IEEE OCEANS 2013, IEEE, 2013: 1-10. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286411135_Hadal_landers_The_DEEPSEA_CHALLENGE_ocean_trench_free_vehicles [61] OLSON R J, SOSIK H M. A submersible imaging-in-flow instrument to analyze nano-and microplankton:imaging flow cytobot[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods, 2007, 5(6):195-203. doi: 10.4319/lom.2007.5.195 [62] 付强, 姜会林, 王晓曼, 等.空间金宝搏188软件怎么用 通信研究现状及发展趋势[J].中国光学, 2012, 5(2):116-125. //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract8803.shtmlFU Q, JIANG H L, WANG X M, et al.. Research status and development trend of space laser communication[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(2):116-125.(in Chinese) //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract8803.shtml [63] SIERACKI M E, BENFIELD M, HANSON A, et al.. Optical plankton imaging and analysis systems for ocean observation[J]. Proceedings of Ocean OBS, 2010, 9:21-25. https://www2.whoi.edu/staff/hsosik/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2017/03/Sieracki_etal_OceanObs2009.pdf [64] SCHMID M S, AUBRY C, GRIGOR J, et al.. The LOKI underwater imaging system and an automatic identification model for the detection of zooplankton taxa in the Arctic Ocean[J]. Methods in Oceanography, 2016, 15:129-160. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301891643_The_LOKI_underwater_imaging_system_and_an_automatic_identification_model_for_the_detection_of_zooplankton_taxa_in_the_Arctic_Ocean [65] BRISE O-AVENA C, ROBERTS P L D, FRANKS P J S, et al.. ZOOPS-O 2:A broadband echosounder with coordinated stereo optical imaging for observing plankton in situ[J]. Methods in Oceanography, 2015, 12:36-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mio.2015.07.001 [66] MULLEN A D, TREIBITZ T, ROBERTS P L D, et al.. Underwater microscopy for in situ studies of benthic ecosystems[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7:12093. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12093 [67] JOHNSE G, VOLENT Z, DIERSSEN H, et al.. Underwater hyperspectral imagery to create biogeochemical maps of seafloor properties[J]. Subsea Optics and Imaging, 2013:508-535 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780857093417500200 -






 下载:
下载: