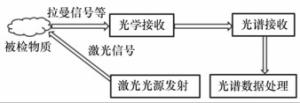
-
摘要: 远距离检测主要用于人类不宜或不易接触的物品检测,紫外拉曼光谱法是一种比较有效的远距离危险物品检测方法,在反恐、禁毒和食品安全等领域具有广泛的应用前景。本文在分析远程拉曼光谱检测技术基本原理的基础上,总结了紫外拉曼光谱检测技术的优势,对远程紫外拉曼光谱检测技术的现状进行综合分析。从金宝搏188软件怎么用 器发射、光学接收系统、光谱接收、光谱处理等方面分析了不同模块关键技术及研究现状,分析了远程紫外拉曼光谱检测技术的研究难点和发展趋势。Abstract: Ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy is a relatively effective and promising method for the detection of long-distance dangerous items. It has broad applications in the fields of anti-terrorism, drug control and food safety. Based on an analysis of the basic principles of Raman spectroscopy remote detection, this paper summarizes the advantages of ultraviolet Raman detection technology and comprehensively analyzes its research status. The module's design methods, key techniques and existing problems are analyzed from the perspective of laser emission, optical receiving system, spectral reception and spectral processing. The research difficulties and development trends of remote detection technology with ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy are summarized.
-
Key words:
- ultraviolet /
- Raman spectroscopy /
- remote detection /
- spectral processing
-
表 1 常规紫外拉曼系统金宝搏188软件怎么用 光源参数及探测目标参数
Table 1. Laser source and target parameters of conventional UV Raman system
光源参数 目标参数 参考文献 光源波长/nm 光源能量 目标距离/m 目标类型 尺寸或含量 228 >0.5 μJ/pulse,5 mW, 0~10 kHz 1~10 explosives 1 mm×1 mm~200 mm×200 mm [15] 229 CW, 4.3 mW 2.3 PETN, AN 10~1 000 μg/cm2 [46] 262 3 mW/cm2, 500 Hz 1~10 sucrose等 / [23] 266 3 mJ/cm2, 20 Hz 6~10 AN 100 μg/cm2 [17] 266 10.3 mJ/pulse, 10 Hz 18 KClO3, calcite / [24] 266 23.5 mJ/pulse, 10 Hz 42 Teflon 2 mm厚, 30 mm×30 mm的立方体 [19] 266 8 mJ/pulse, 30 Hz 533 Teflon/cyclohexane, acetonitrile 850 g/m2 [5] 355 13 mW, 100 Hz 6 有机物等 / [41] 355 1.5 mJ/pulse, 1 kHz 10 AN 单个AN微粒直径<300 μm [18] 220, 232, 248, 250, 260等波长可调 3~10 mJ/pulse, 10 Hz 13 NM, AN / [12] 其中CW为连续金宝搏188软件怎么用 器,表中的“/”代表文献中未提到该项参数. 表 2 常规光学接收系统参数及目标距离
Table 2. Conventional optical receiving system parameters and target distance
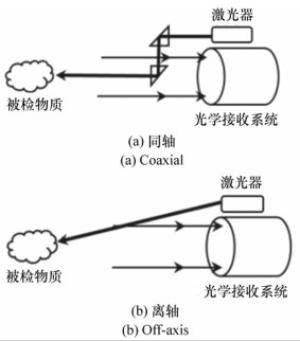
光学接收系统 目标距离/m 参考文献 几何结构 光学结构 直径 F数 焦距/mm coaxial Cassegrain 1.6 in. f/15 / 533 [5] coaxial Cassegrain 203 mm 10 2 032 22 [8] coaxial Cassegrain 203.2 mm / / 6 [41] coaxial Schmidt-Cassegrain 200 mm / 300 10 [18] coaxial Newtonian 6 in. f/4 / 30 [6] coaxial Newtonian 300 mm / 1 000 6~10 [17] coaxial Richey Chretien 12.4 in. f/9.1 / 18 [24] coaxial Gregorian 6 in. / / / [34] off-axis Cassegrain / / / 13 [12] / Maksutov-Cassegrain 3.5 in. / / 2.3 [46] / Schmidt-Cassegrain 8 in. / / 30 [22] 表 3 现有远程紫外拉曼光谱检测系统光谱接收模块参数
Table 3. Spectral receiver module parameters of current remote ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy system
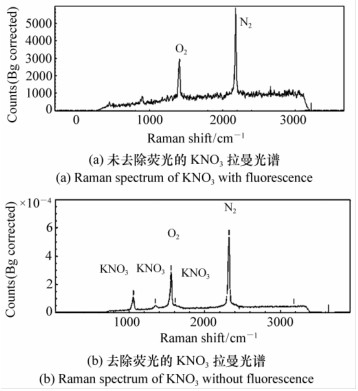
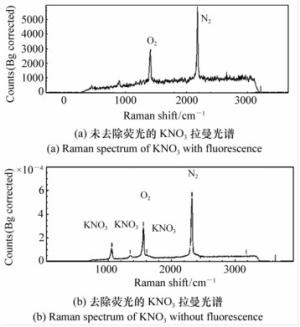
光谱分辨率/cm-1 光栅分辨率 光谱范围/cm-1 信噪比 探测器 参考文献 3 300 grooves/mm, 300 nm / / gated ICCD [24] 4.5 600、2 400、1 800 grooves/mm 800~1800, 2 500-4 000 / ICCD [10] 10 / / / gated ICCD [18] 11 2 400 grooves/mm, 250 nm / 5:1 gated ICCD [5] 15 / / 13:1 gated ICCD [23] 22 2 380 grooves/mm 650~3 650 / gated ICCD [6] 30 3 600 line/mm <3443 / ICCD [34] 40 1 200, 2 400 grooves/mm 100~2 100, 300~4 300 / gated ICCD [41] -
[1] COONEY J. Satellite observation using Raman component of laser backscatter[C]. Proceedings of the Symposium of Electromagnetic Sensing of the Earth from Satellites, Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn Press, 1967: P1-P10. [2] LEONARD D A. Observation of Raman scattering from the atmosphere using a pulsed nitrogen ultraviolet laser[J]. Nature, 1967, 216(5111):142-143. doi: 10.1038/216142a0 [3] HIRSCHFELD T. Range independence of signal in variable focus remote Raman spectrometry[J]. Applied Optics, 1974, 13(6):1435-1437. doi: 10.1364/AO.13.001435 [4] MEASURES R M. Laser Remote Sensing:Fundamentals and Applications[M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons, 1984. [5] WU M, RAY M, FUNG H, et al.. Stand-off detection of chemicals by UV Raman spectroscopy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2000, 54(6):800-806. doi: 10.1366/0003702001950418 [6] RAY M D, SEDLACEK A J, WU M. Ultraviolet mini-Raman lidar for stand-off, in situ identification of chemical surface contaminants[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2000, 71(9):3485-3489. doi: 10.1063/1.1288255 [7] RAMAN C V, KRISHNAN K S. A new type of secondary radiation[J]. Nature, 1928, 121(3048):501-502. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_39a2eee3860202c1b00175b16edc577f [8] FULTON J. Remote detection of explosives using Raman spectroscopy[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8018:80181A. doi: 10.1117/12.887101 [9] SMITH E, DENT G. Modern Raman Spectroscopy:A Practical Approach[M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons, 2013. [10] BYKOV S, LEDNEV I, IANOUL A, et al.. Steady-state and transient ultraviolet resonance Raman spectrometer for the 193-270 nm spectral region[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2005, 59(12):1541-1552. doi: 10.1366/000370205775142511 [11] CLARK R J H, DINES T J. Resonance Raman spectroscopy, and its application to inorganic chemistry. New analytical methods (27)[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 1986, 25(2):131-158. doi: 10.1002/anie.198601311 [12] PETTERSSON A, WALLIN S, STMARK H, et al.. Explosives standoff detection using Raman spectroscopy:from bulk towards trace detection[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7664:76641K. doi: 10.1117/12.852544 [13] 周明辉, 廖春艳, 任兆玉, 等.表面增强拉曼光谱生物成像技术及其应用[J].中国光学, 2013, 6(5):633-642. //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9047.shtmlZHOU M H, LIAO CH Y, REN ZH Y, et al.. Bioimaging technologies based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and their applications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(5):633-642.(in Chinese) //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9047.shtml [14] ANGEL S M, KULP T J, VESS T M. Remote-Raman spectroscopy at intermediate ranges using low-power cw lasers[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1992, 46(7):1085-1091. doi: 10.1366/0003702924124132 [15] MCCAIN S T, GUENTHER B D, BRADY D J, et al.. Coded-aperture Raman imaging for standoff explosive detection[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8358:83580Q. doi: 10.1117/12.919292 [16] CHIRICO R, ALMAVIVA S, BOTTI S, et al.. Stand-off detection of traces of explosives and precursors on fabrics by UV Raman spectroscopy[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8546:85460W. doi: 10.1117/12.974518 [17] ALMAVIVA S, ANGELINI F, CHIRICO R, et al.. Eye-safe UV Raman spectroscopy for remote detection of explosives and their precursors in fingerprint concentration[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9253:925303. doi: 10.1117/12.2067292 [18] GLIMTOFT M, BM··TH P, SAARI H, et al.. Towards eye-safe standoff Raman imaging systems[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9072:907210. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLHY/NSTL_HYCC0214507207/ [19] CARROLL J A, IZAKE E L, CLETUS B, et al.. Eye-safe UV stand-off Raman spectroscopy for the ranged detection of explosives in the field[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2015, 46(3):333-338. doi: 10.1002/jrs.4642 [20] PATRICK C, CAL C J, JEAN D R, et al.. Detection of explosives on surfaces using UV Raman spectroscopy: effect of substrate color[R]. US Army Research Laboratory Adelphi United States, 2017. [21] GAFT M, NAGLI L. Standoff laser-based spectroscopy for explosives detection[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6739:673903. doi: 10.1117/12.736631 [22] GAFT M, NAGLI L. UV gated Raman spectroscopy for standoff detection of explosives[J]. Optical Materials, 2008, 30(11):1739-1746. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2007.11.013 [23] HOPKINS A J, COOPER J L, PROFETA L T M, et al.. Portable deep-ultraviolet(DUV) Raman for standoff detection[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2016, 70(5):861-873. doi: 10.1177/0003702816638285 [24] LAMSAL N, SHARMA S K, ACOSTA T E, et al.. Ultraviolet stand-off Raman measurements using a gated spatial heterodyne Raman spectrometer[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2016, 70(4):666-675. doi: 10.1177/0003702816631304 [25] 张莉, 郑海洋, 王颖萍, 等.远距离探测拉曼光谱特性[J].物理学报, 2016, 65(5):054206. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201605017ZHANG L, ZHENG H Y, WANG Y P, et al.. Characteristics of Raman spectrum from stand-off detection[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(5):054206.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201605017 [26] 姚齐峰, 王帅, 夏嘉斌, 等.远距离物质拉曼光谱探测系统[J].红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程, 2016, 45(11):1103001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201611001YAO Q F, WANG SH, XIA J B, et al.. Remote Raman spectrum detection system of material[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(11):1103001.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201611001 [27] GULATI K K, GAMBHIR V, REDDY M N. Detection of nitro-aromatic compound in soil and sand using time gated Raman spectroscopy[J]. Defence Science Journal, 2017, 67(5):588-591. doi: 10.14429/dsj.67.10290 [28] FARLEY Ⅲ C, KASSU A, BOSE N, et al.. Short distance standoff Raman detection of extra virgin olive oil adulterated with canola and grapeseed oils[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2017, 71(6):1340-1347. doi: 10.1177/0003702816681796 [29] 刘凯, 陈荣利, 常凌颖, 等.共口径双通道红外扫描成像光学系统[J].应用光学, 2012, 33(2):395-401. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201202031LIU K, CHEN R L, CHANG L Y, et al.. Common-aperture dual-channel infrared scanning imaging optical system[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2012, 33(2):395-401. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201202031 [30] 巩盾, 王红, 田铁印.多种应用于高功率金宝搏188软件怎么用 技术的光学系统设计[J].红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程, 2013, 42(S1):118-122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc2013z1024GONG D, WANG H, TIAN T Y. Optical design of various optical systems applied in high power laser technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(S1):118-122.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc2013z1024 [31] 殷笑尘, 付彦辉.红外/金宝搏188软件怎么用 共孔径双模导引头光学系统设计[J].红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程, 2015, 44(2):428-431. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.02.005YIN X CH, FU Y H. Optical design of common aperture IR/ladar dual-mode imaging seeker[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(2):428-431.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.02.005 [32] 贾冰, 曹国华, 吕琼莹, 等.多谱段共孔径跟踪/引导系统光学设计[J].红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程, 2017, 46(2):0218001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hwyjggc201702025JIA B, CAO G H, LV Q Y, et al.. Optical design of tracking/guiding system with multi-spectrum and common aperture[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(2):0218001.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hwyjggc201702025 [33] 王帅, 姚齐峰, 董明利, 等.远程金宝搏188软件怎么用 拉曼光谱探测系统前置光学系统设计[J].红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程, 2018, 47(4):0418004. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201804029WANG SH, YAO Q F, DONG M L, et al.. Fore optical system design for remote laser Raman spectrum detection system[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(4):0418004.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201804029 [34] HA Y C, LEE J H, KOH Y J, et al.. Development of an ultraviolet Raman spectrometer for standoff detection of chemicals[J]. Current Optics and Photonics, 2017, 1(3):247-251. [35] 胡广骁, 熊伟, 罗海燕, 等.用于远程探测的空间外差拉曼光谱技术研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(12):3951-3957. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201612025HU G X, XIONG W, LUO H Y, et al.. The research of spatial heterodyne raman spectroscopy with standoff detection[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(12):3951-3957.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201612025 [36] ROESLER F L, HARLANDER J M. Spatial heterodyne spectroscopy:interferometric performance at any wavelength without scanning[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1990, 1318:234-244. doi: 10.1117/12.22119 [37] CARTER J C, ANGEL S M, LAWRENCE-SNYDER M, et al.. Standoff detection of high explosive materials at 50 meters in ambient light conditions using a small Raman instrument[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2005, 59(6):769-775. doi: 10.1366/0003702054280612 [38] LAMSAL N, BARNETT P, ANGEL S M, et al.. Remote UV Raman spectroscopy for planetary exploration using a miniature spatial heterodyne Raman spectrometer[C]. Proceedings of the 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 2016: 1500. [39] COOPER J, HOPKINS A J, PROFETA L T M, et al.. Deep ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy for eyesafe standoff chemical threat detection[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10637:1063714. [40] 王欢, 王永志, 赵瑜, 等.拉曼光谱中荧光抑制技术的研究新进展综述[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(7):2050-2056. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201707013WANG H, WANG Y ZH, ZHAO Y, et al.. Latest methods of fluorescence suppression in Raman spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(7):2050-2056.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201707013 [41] SKULINOVA M, LEFEBVRE C, SOBRON P, et al.. Time-resolved stand-off UV-Raman spectroscopy for planetary exploration[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2014, 92:88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2014.01.010 [42] 姜承志.拉曼光谱数据处理与定性分析技术研究[D].长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2014.JIANG CH ZH. Research on data processing and qualitative analysis of Raman spectrum[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014.(in Chinese) [43] 侯岩.基于相关系数与局部信噪比的拉曼谱峰识别技术研究[D].成都: 电子科技大学, 2017.HOU Y. Based on correlation coefficient and local SNR Raman spectra recognition technology research[D]. Chengdu: School of Astronautics & Aeronautics, 2017.(in Chinese) [44] 夏嘉斌, 祝连庆, 姚齐峰, 等.基于Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验的远程拉曼光谱寻峰算法[J].仪器仪表学报, 2018, 39(3):141-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yqyb201803017XIA J B, ZHU L Q, YAO Q F, et al.. Remote Raman spectral peak searching algorithm based on Kolmogorov-Smirnov test[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2018, 39(3):141-147.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yqyb201803017 [45] HAGEN N, BRADY D J. Coded-aperture DUV spectrometer for stand-off Raman spectroscopy[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7319:73190D. doi: 10.1117/12.818830 [46] HUFZIGER K T, BYKOV S V, ASHER S A. Ultraviolet Raman wide-field hyperspectral imaging spectrometer for standoff trace explosive detection[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2017, 71(2):173-185. doi: 10.1177/0003702816680002 [47] YELLAMPALLE B, MARTIN R, WITT K, et al.. Performance comparison of single and dual-excitation-wavelength resonance-Raman explosives detectors[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10183:101830E. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6308e6a7e375924c4d87cd967fe358f3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn -





 下载:
下载: